The procedure for disassembling Interskol rotary hammers
In recent years, Interskol hammer drills have become especially popular. They are reliable in operation and easy to repair. It's easy to get spare parts for them.
Interskol rotary hammers have a wide selection. The tools are conventionally divided into two sectors: hammer drills equipped with an SDS-plus type chuck, and hammer drills with an SDS-max type chuck.
Repair of the Interskol rotary hammer can be carried out both in service centers and without the help of others. To repair Interskol rotary hammers on your own, you need to have the skills of a mechanic and knowledge of electrical engineering at the level of high school.
And always remember to follow safety regulations.
Whoever has a tool with a corresponding marking plate. For example: hammer drill Interskol P-18/450Er. Stands for:
- the letter P indicates that the tool belongs to the family of hammer drills;
- number 18 shows that with this hammer drill a drill with a diameter of up to 18 mm is used;
- the number 450 shows the power of the rotary hammer in watts.
The line of Interskol rotary hammers with SDS-plus cartridges is represented by 13 models: P-18/450ER, P-20/550ER, P-22/620ER, P-24/700ER, P-24/700ER-2, P-26/ 750EV, P-26/800ER, P-26/800ER-2, P-28/800EV, P-30/900ER, P-30/900ER-2, P32/1000E, P-32/1000EV-2.
Interskol rotary hammers with SDS-max cartridges are represented by the following models: Interskol P-35/1100E, P-35/1100EV-2, P-40/110EV-2, P-45/1100E, P-50/1200E.
Interskol rotary hammers are considered on the economic market
: Interskol P-600 ER and
Interskol P-710 ER.
These models were carried out at the beginning of the production development of the Interskol office. Among household users, the most common models are the Interskol P26/800ER, P30/900ER, P710/ER rotary hammers.
Disassembling Interskol rotary hammers models P18, P22, P26, P28, P30, P600, P710
The operating mechanism of all rotary hammers is similar.
The torque from the rotor is transmitted to the barrel shaft and the working tool attached to it. Immediately, in the presence of a swinging bearing, simply called a “drunk bearing,” the torque is converted into a reciprocating motion, transmitting a shock impulse to the working tool.
Our client is left with Interskol rotary hammers assembled according to one general scheme and consisting of the same blocks.
Conventionally, Interskol rotary hammers consist of 3 blocks:
- Impact unit gearbox unit.
- Stator block.
- Power and control circuit block.
Repair of Interskol rotary hammers should begin with a study of the tool diagram, preparation of tools and the working area.
The designated blocks of the listed models have their own design features.
For ease of consideration, we will divide the exposed rotary hammers into groups.
- In the first group we will include Interskol P-18, P-22, P-24, P-26, P-30 rotary hammers.
- In the next group we will look at the disassembly of the Interskol P-600 and P710 hammer drills.
Replacing brushes
If it’s time to change the brushes in a hammer drill, you can take the tool to a service center for this task, or you can do it yourself, which is quite easy. Replacement at a service center has a number of advantages:
- High-quality work if it is a specialized center
- Original parts for your tool model
- Extending the warranty if the period has not yet expired
- In addition to replacing the broken part, the service usually inspects the entire internal important parts, cleans them and lubricates them
Along with the advantages, repairing power tools at a service center also has disadvantages:
- If there is no guarantee, the work will be paid for
- Repairs will take time, you'll have to wait
- Service is not always close
If you are not satisfied with the indicated inconveniences of repairing a tool in a specialized center, it is better to complete the task yourself.
The process of replacing parts is carried out in stages:
- The hammer drill, which is disconnected from the socket, must be unscrewed to remove the top cover.
- After this, using a small screwdriver, you need to easily hook the brush holder, remove it and remove the old parts.
- Insert new ones into the holder, press them to the edges, and place them in place inside the hammer drill.
- Check that the brushes reach the contacts for smooth operation of the power tool.
- Close the lid and secure it with screws.
Tips from experts when repairing a rotary hammer
When replacing brushes yourself, experts recommend:
- When one is erased, both must be replaced.
- During repairs, it is also necessary to clean the collector from dust and carbon deposits.
- When replacing a part, it is better to grind it to the collector using fine-grained sandpaper
- It is better to install components that match the tool model
Replacing hammer drill brushes is a simple process that can be easily done at home.
Disassembling the keyless chuck
Let's look at disassembling a quick-release chuck using the example of an Interskol P-26/800ER hammer drill.
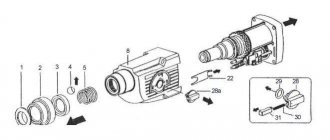
Having installed the hammer drill on the back of the handle, you need to remove the protective sleeve pos. 1, remove the washer pos. 2 and remove the locking ring pos. 3.
Next, remove the washer pos. 4 and the retaining ring pos. 5. Next, the pressure sleeve pos. 6 is removed.
To release the fixing ball pos. 8, you need to press on the special washer pos. 9. Pull out the ball, take out the conical spring pos. 10.
The design of the quick-release chuck for the Interskol P-30/900ER hammer drill contains the least number of parts. But the disassembly procedure remains the same.
The quick-release chucks for the Interskol P-600ER and P-710ER rotary hammers are virtually the same and are disassembled in a similar sequence.
Keyless chuck for rotary hammer Intersol P-30/900ER
The parts of the quick-release chuck for the Interskol P600ER and P710ER rotary hammers are dismantled in the following order:
- the special ring pos. 1 is removed;
- release sleeve position 2 is released;
- press the special ring pos. 3 and take out the ball pos. 4;
- the spiral spring pos. 5 is removed.
For all Interskol rotary hammers, to remove the gear housing, you must first remove the mode switch.
Disassembling the impact mechanism of the Interskol P-26/800ER hammer drill
In the Interskol P-26/800ER hammer drill, the impact mechanism consists of the following components:
- tool receiver;
- barrel pressing unit;
- trunk;
- intermediate shaft;
- strikers, drummers, industrial mass.
Disassembling the tool receiver
The tool receiver pos. 12 is disassembled after removing the parts of the quick-release chuck from it.
Initially, four rollers, position 11, are carefully removed. Next, the receiver is removed from the housing, pos. 18, into which the needle bearing, pos. 20, is inserted.
The barrel, pos. 36, is attached to the needle bearing.
Pull the tool receiver out of the barrel.
From the tool receiver you need to remove the industrial mass pos. 16, the bushing pos. 15, the cuff pos. 14 and the rubber sealing ring pos. 13.
Mechanical group of faults in Interskol rotary hammers
Let's look at all the faults using the example of the Interskol P-26/800ER rotary hammer.
The first group of malfunctions includes breakdowns associated with the failure of parts of the impact mechanism.
This group of malfunctions manifests itself in the fact that during operation the hammer drills, but cannot chisel.
Wear of rubber sealing rings
The weakening of the impact force occurs gradually. As the rubber rings wear, air leaks into the pneumatic shock system. The force of the blow weakens, the blow becomes hard. In addition to the loss of pneumatic properties, the destruction of strikers, strikers, and press masses occurs.
Set of rubber sealing rings for the Interskol hammer drill
Repair of an Interskol hammer drill when the sealing rings are worn out consists of replacing them with new ones.
Installation of new rubber rings is carried out during any disassembly of the hammer drill with the obligatory application of lubricant to the sealing rings with lubricants that are inert to rubber products. Such lubricants include the domestic lubricant type Tsiatim-224, produced in accordance with GOST 9433-80.
The rubber sealing ring is lubricated with a thin layer of Tsiatim-224 lubricant and put on the desired part, which has previously been washed from the old lubricant in a solution of a mixture of kerosene and gasoline.
Destruction of strikers, drummers, barrels, pistons
If the rubber sealing rings are worn out and are not replaced in a timely manner, the molding material pos. 16, the barrel pos. 36, the catcher body pos. 40, and the striker pos. 45 are destroyed. The impact causes hardening, cracks, bending, and jamming to appear on parts.
Malfunctions are eliminated by replacing parts with new ones with the obligatory change of seals.
Details of the impact block of the Interskol P-26/800ER hammer drill
There are two types of destruction of the piston pos.47:
- The piston skirt is destroyed;
- The ears of the finger installation, pos. 48, break off.
Repair of the Interskol P-26/800ER rotary hammer and its damaged piston is carried out by replacing the piston with a new one. When purchasing a piston, carefully check the roughness of the inner surface of the piston. It should be brought to a mirror shine.
Disassembling the barrel of the percussion mechanism
The barrel, pos. 36, is removed from the internal housing, pos. 18, if the gearbox housing separates from the stator housing. For this purpose, you need to remove four screws, pos. 30, from the gearbox housing.
Then unscrew the three screws pos. 85 on the handle pos. 86. After removing the handle, turn the brush holder housing pos. 81. until the moment when it is of course removed from the case.
Now the gearbox housing and the stator housing are simply divided using a screwdriver, which is used to pry off one of them at the junction.
The barrel is simply removed from the industrial shield, pos. 53 (inner housing).
Mounted on the outer diameter of the barrel are: spur gear pos. 35, spring pos. 33, washer pos. 32 and retaining ring pos. 31.
In the barrel cavity there is a body of the catcher, position 40, and a firing pin 45.
Dismantling the intermediate shaft
To disassemble the intermediate shaft pos. 57, you need to remove it from the inner housing. From the shaft pos. 58, remove the switch arm pos. 55 and the spring pos. 56.
On the other side: remove the support bushing pos. 65, the spring support pos. 64, the spring pos. 63, the combined gear wheel pos. 62.
Intermediate shaft of the Interskol P-26/800ER rotary hammer Catalog of spare parts for the intermediate shaft of the Interskol P-26/800ER rotary hammer
Disassembling the impact mechanism of the Interskol P710ER hammer drill
The design of the impact mechanism and the disassembly procedure for the Interskol 710ER rotary hammer are somewhat different from rotary hammers of other models.
The main differences are in the design of the intermediate shaft, the barrel of the impact mechanism and the mode switch.
Diagram of the impact mechanism and the intermediate shaft of the Interskol P710ER
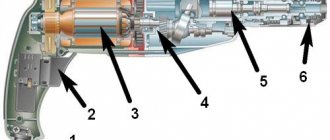
The Interskol 710ER rotary hammer is a rotary-impact machine. Consists of an electric drive and an actuator. For electric drive, a commutator motor is used. The actuator is essentially a combination of a compression-vacuum type impact mechanism and a rotational mechanism. The reciprocating motion is transmitted by a rolling bearing.
The diagram shows the procedure for disassembling the barrel, position 15 (indicated by a reddish arrow), the composition of the strikers and strikers (indicated by a blue arrow). The greenish arrow indicates the details of the mode switch.
The intermediate shaft consists of shaft pos. 47 and parts mounted on it. It is easy to understand, according to the attached diagram, and does not require any special knowledge.
The structure of the tool and its mechanism
The functional purpose of a hammer drill is determined by its internal structure.
The reinforced shock-rotational mechanism of the tool is the so-called “oscillating bearing” or “crank rod”, which, rotating from the engine, transmits vibrations to the pneumatic pistons (or piston), after which the air pumped into the pistons pushes the striker with a blow.
An impact force of 17-20 kilojoules and parallel rotation of the displacer due to the transmission gear ensures that the chisel or drill enters high-density material. It is necessary for punching through holes or drilling holes for electrical wiring or plumbing pipes.
Video about the construction of a hammer drill and impact mechanism:
Disassembling the electronic part of the Interskol hammer drill
The electronic part of the Interskol hammer drill consists of 3 main parts:
- rotor;
- stator;
- control circuits with carbon brushes.
The procedure for disassembling the electronic part of all models of Interskol rotary hammers is virtually the same.
Electronic circuit of the hammer drill Interskol P-26/800ER
In the previous steps, we divided the housing into two: the gearbox housing and the stator housing.
Interskol rotary hammer assembly video
Assembling the INTERSKOL P-18/450ER rotary hammer
Assembling the INTERSKOL P-22/600ER hammer drill
Assembling the INTERSKOL P-26/800ER hammer drill
Assembling the INTERSKOL P-600ER hammer drill
Assembling the INTERSKOL P-710ER hammer drill
Correct operation of the Makita 2450 rotary hammer with a commutator motor is accompanied by slight sparking of the brushes in the commutator area. It's fine.
Today, metal fences are very popular among owners of country houses. Before building a fence from corrugated board.
In the interior of any room, curtains play an important role: they not only protect the inhabitants from bright sun or dust, but also decorate our lives.
Disassembling control circuits and dismantling carbon brushes
The control base for the Interskol hammer drill is the switch pos. 87 and the reverse lock pos. 90. Using the combination button, the hammer drill has the option to set the speed of the electric motor.
To get the brushes pos. 83, you need to remove the brush holder pos. 81. It is removed by turning it counterclockwise by 90º. Having released the brush holder, the carbon brushes are easy to remove.
The design of the Interskol P710ER and P600ER rotary hammers has its own characteristics:
- there is no combined brush holder;
- a different type of switch is used.
It remains for our client! The Interskol hammer drill has been disassembled. Read the instructions for repairs and how to assemble and lubricate the hammer drill.
Source