Nickel-cadmium batteries (NiCd) are a fairly common type of energy storage device that has found its application in various fields. Naturally, like other types of batteries, NiCd have their own positive and negative sides, which make them more or less acceptable in certain cases. They often service household appliances, electrical appliances, transport, and are even used in aviation. In this topic, we will discuss these wonderful power supplies in detail.
History of invention
NiCd was invented back in 1899 by the Swede Waldemar Jungner. The positive electrode was made of nickel, and the negative electrode was made of cadmium. Two years later, the famous inventor Thomas Edison made his contribution to the common cause by proposing an alternative scheme. The scientist decided to use iron instead of cadmium. Nickel-cadmium and nickel-iron systems were, let’s say, not cheap, so their practical use was limited.
Technical progress, as they say, does not stand still, and after the appearance of the compressed anode in 1932, a large number of upgrades were made. As a result, the developers received increased load current and a longer service life. Sealed NiCd, which is quite common today, became a reality after the creation of a completely sealed element, and this significant event occurred in 1947.
Nickel-cadmium batteries - what are they, history of creation
The battery was created by Wagner Junger in 1899. But due to the high cost of extracting the materials used, further development was postponed. It gained great popularity in use after 1932, when a method was invented to deposit the active substance on a nickel electrode. Since 1947, when scientists developed a method for restoring gases inside a battery when charging, they began to produce batteries in a sealed case. We see these now in electrical appliances.
Ni cad batteries consist of two oppositely charged electrodes separated by a separator. All elements are placed in an electrolyte and are in a sealed housing made of plastic or metal.
Unlike other batteries, nickel batteries do not overheat due to their low resistance, which reduces the possibility of overheating. It heats up only after full charging, as an indicator of the end of the charge.
Scope of application
Widely used for household appliances and equipment that consume large amounts of current. In portable equipment: screwdrivers and drills. In public transport they are used to power the control circuits of trolleybuses and trams, and in sea and river transport and aircraft as a secondary source of raw materials. Advantages of use: durable, easy to maintain, lightweight and almost insensitive to low temperatures.
Cons: contain poisonous cadmium, not environmentally friendly. It is forbidden to dispose of it in household waste; you must use special containers for recycling batteries.
Device and principle of operation
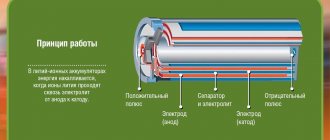
The Ni-Cd energy storage device has two electrodes: nickel and cadmium. The positive electrode is a nickel hydroxide paste connected to a conductive material and applied to a steel mesh, and the negative electrode is made in the form of a steel mesh with cadmium sponge pressed into it. The role of the electrolyte is played by a highly active alkali, which is not explosive. Also, it doesn't smell like anything. All this is hermetically packaged in a metal or plastic case, which can have a flat, cubic or cylindrical shape.
In the production of electrodes, metal foiling is used, which allows increasing the contact area. Separators are made of material that does not dissolve in alkali. They do not interfere with the free movement of electrolyte between the electrodes. A chemical process takes place inside the NiCd electronic storage device, which involves hydroxides of nickel, cadmium and water. This process is reversible.
At the top of the battery there are current-collecting contacts, through which individual components can be connected into blocks. The lid has a hole with a plug so that alkali can be added and, in addition, through this hole, excess gases evaporate while charging the energy source.
Based on the type of design, storage devices with cadmium electrodes are divided into two types:
- Prismatic. The electrodes are made as plates and are stacked on top of each other through a separator.
- Cylindrical. Electrodes are manufactured as tape and rolled into rolls. The positive and negative electrodes are also separated by a separator.
Operating principle and design of Ni-Cd battery
These batteries produce electrical energy through the reversible process of interaction of cadmium (Cd) with nickel oxide-hydroxide (NiOOH) and water, which results in the formation of nickel hydroxide Ni(OH)2 and cadmium hydroxide Cd(OH)2, which causes the appearance of electromotive force.
Ni-Cd batteries are produced in sealed cases containing electrodes separated by a neutral separator containing nickel and cadmium in a solution of a jelly-like alkaline electrolyte (usually potassium hydroxide, KOH).
The positive electrode is a steel mesh or foil coated with nickel oxide-hydroxide paste mixed with conductive material
The negative electrode is a steel mesh (foil) with pressed porous cadmium.
One nickel-cadmium cell is capable of producing a voltage of about 1.2 volts, so to increase the voltage and power of batteries, their design uses many parallel-connected electrodes separated by separators.
Specifications
☑ Minimum discharge voltage - 0.9 V.
☑ Normal operating voltage is 1.2 V. If you need to organize a voltage of 24 V and 12 V, individual components are assembled into blocks by connecting them in series.
☑ The voltage in a NiCd electronic storage device at 100% charge is 1.5 V.
☑ NiCd can operate in a temperature range of -50...+40 degrees, which certainly sets such equipment apart from its competitors.
☑ Depending on the conditions in which the equipment is operated, a Ni-Cd battery can withstand up to 2000 cycles.
☑ Self-discharge reaches 25% of the starting capacity.
☑ Specific energy capacity up to 65 W*h/kg.
☑ Nickel-cadmium lasts up to ten years. But that's not all: modern lamella industrial NiCd batteries can last 20-25 years!
Differences between Li-Ion and Ni-Cd batteries
Let's compare the following characteristics: the essence of electrochemical processes, environmental impact, cost, operating features and performance, as well as practical application.
A nickel-cadmium battery uses cadmium as the anode (negative terminal), nickel oxyhydroxide as the cathode (positive terminal), and aqueous potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte.
A lithium-ion battery uses graphite as the anode, lithium oxide as the cathode, and lithium salt as the electrolyte. Lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge, and in the opposite direction during charging.
| Name | Li-Ion power supplies | Ni-Cd power supplies |
| Voltage | 3.6/3.7 V | 1.2V |
| Number of working cycles | Up to 1200 | Until 2000 |
| Charge/discharge efficiency | 80…90 % | 70…90 % |
| Temperature dependence of the intensity of the self-discharge process (per month) | Up to 8% at 21°C Up to 15% at 40°C Up to 31% at 60°C | To 10% |
| Energy density | 250…620 W h/l | 50…150 W h/l |
| Disposal | Little hazardous waste | Hazardous waste |
Ni-Cd batteries contain between 6% (for industrial sources) and 18% (for consumer batteries) cadmium, which is a toxic heavy metal and therefore requires special care when removing and disposing of the used battery. Such waste is considered environmentally hazardous. At the same time, all components of lithium-ion batteries are environmentally friendly, since lithium is a non-toxic metal.
In terms of cost, a lithium-ion battery costs about 40% more than a nickel-cadmium battery. This is due to the significant manufacturing costs of providing additional protection circuitry that monitors voltage, current and power parameters.
Li-Ion 3.6v
Advantages and disadvantages
Naturally, like other power sources, nickel-cadmium has its positive and negative sides. In some areas, such energy storage devices are difficult to replace with anything, so until more advanced technologies are released, NiCd will continue to perform its functions for a long time, because their performance characteristics are quite competitive.
pros
✅ Wide range of operating temperatures (-50...+40 degrees, can be charged at temperatures below zero). True, there is no reliable information regarding how the equipment will behave at such low temperature conditions!
✅ Can be stored for a long time in a discharged state.
✅ Can withstand many discharge/charge cycles.
✅ Security. If we compare Li-ion, then NiCd cannot ignite when depressurized. They are also safe during transportation - they are accepted as cargo by airlines without any problems.
✅ Low resistance. It is for this reason that the product will not heat up during charging even if a high current is applied. The battery begins to heat up when it is “filled up” to capacity, which is a signal for the end of the charging process.
✅ Functions relatively stably even with a strong minus.
✅ “Flexible” form factor. Can be created in different sizes for different installation options.
✅ Affordable. This is the cheapest type of electronic storage device when calculated per cycle.
Minuses
⛔ Quite a high level of independent discharge. A NiCd power source can lose up to 10% of its capacity in the first day, and after one or two months, the electronic storage device will be discharged to zero. However, there are NiCd models on the market whose capacity loss is only 10-12% per month. It also matters how charged the battery is.
⛔ After prolonged storage without activity, Ni-Cd will need to be restored using a special method.
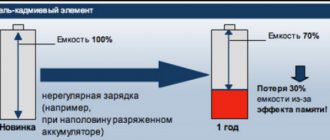
⛔ NiCd must be brought to full discharge, as they have a clearly expressed memory effect.
⛔ Nickel-cadmium has low energy density.
⛔ Ni-Cd energy storage devices need periodic “training”: 3-4 charges/discharges for recovery.
⛔ Smaller capacity with greater mass, when compared with alternative types of energy sources with the same dimensions.
⛔ Low voltage with a decrease from 1.5 V (at the first 10%) to 1.2 V (a large number of elements will be required to create a high voltage).
The issue of memory effect is worth discussing in more detail, since it is one of the features of NiCd batteries. The device remembers the voltage to which it was previously discharged and during the next cycle it will release energy only up to this value. If the battery charge is half used and the unit is set to charge, its capacity will drop by 50 percent. This circumstance will have to be taken into account without fail.
One of the disadvantages is the toxic materials present in nickel-cadmium energy storage devices. These batteries cannot simply be thrown into the trash! Cadmium is a poisonous metal and it is for this reason that NiCd batteries are generally prohibited from being produced in some countries, but at the same time, they are allowed to be used there. In principle, if such batteries are not disassembled and if the housing does not collapse, they are not dangerous. Be that as it may, Ni-Cd products must be disposed of according to certain rules, and the procedure for recycling nickel-cadmium itself is very expensive.
Pros and cons of Ni-Cd battery
This type of battery has the following positive characteristics:
- long service life and number of charge-discharge cycles;
- long service life and storage;
- fast charging capability;
- ability to withstand heavy loads and low temperatures;
- maintaining performance in the most unfavorable operating conditions;
- low cost;
- the ability to store these batteries in a discharged state for up to 5 years;
- average overcharge resistance.
At the same time, nickel-cadmium power supplies have a number of disadvantages:
- the presence of a memory effect, manifested in loss of capacity when charging the battery without waiting for complete discharge;
- the need for preventive maintenance (several charge-discharge cycles) to reach the full capacity;
- complete restoration of the battery after long-term storage requires three to four full charge-discharge cycles;
- high self-discharge (about 10% in the first month of storage), leading to almost complete discharge of the battery within a year of storage;
- low energy density compared to other batteries;
- the high toxicity of cadmium, due to which they are banned in a number of countries, including the EU, the need to dispose of such batteries using special equipment;
- greater weight compared to modern batteries.
NiCd marking
▶ The first numbers indicate the number of individual components that form the battery, how many of them are connected in total.
▶ The letters NK or K indicate that you are dealing with a Ni-Cd electronic storage device.
▶ Latin letters L or H indicate the discharge mode of the energy source. L—long discharge, H—short discharge.
▶ The following number indicates the battery capacity.
▶ The letters P(P) let us know that the body of the electronic drive is made of plastic.
▶ K - type of prefabricated structure of the energy source - frame.
Differences between nickel-cadmium and lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride
☑ NiCd, unlike its opponents, has a strongly pronounced memory effect and a more modest specific capacity with identical dimensions.
☑ Ni-Cd batteries are less demanding, operate stably at fairly low temperatures, and are much more resistant to overcharging and overdischarging.
☑ Li-Ion and Ni-Mh are more expensive, but have a lower degree of self-discharge.
☑ Lithium-ion products can serve and be stored for two to three years, and this is several times less compared to NiCd, which can please their owners with a service life of up to ten years.
☑ Nickel-cadmium batteries lose capacity at a rapid rate when operating in buffer mode. In principle, after such misunderstandings, they can be completely brought to their senses through deep discharge and charge. The best option would be not to use Ni-Cd electronic storage devices in devices where they are constantly recharged.
☑ Nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries are identical in charge mode, which makes it possible to use the same charging equipment. However, it is necessary to take into account the fact that Ni-Cd energy storage devices have a much more pronounced memory effect.
As you can see, nickel-cadmium batteries outperform their competitors in some ways, but at the same time, they are inferior to them in some way. In this regard, it is impossible to say for sure which type of battery is better - they are all good in their own way.
Screwdriver with Ni-Cd or Li-Ion battery. What to choose?
In this article we will try to cover only one question - what is the difference between Ni-Cd (Nickel-Cadmium) and Li-Ion (Lithium-Ion) batteries.
There are two models in the Bosch line of cordless screwdrivers that have earned an excellent reputation among consumers for their characteristics as reliable, convenient and durable tools. 1. Cordless drill-driver Bosch GSR 12-2 with Ni-Cd battery; 2. Cordless drill-driver Bosch GSR 10.8-2 with Li-Ion battery.
However, a beginner in using battery technology sometimes asks one of the most significant questions when choosing a screwdriver - which battery to use? Let's look at the main advantages and disadvantages of Ni-Cd (Nickel-Cadmium) and Li-Ion (Lithium-Ion) batteries.
To the main advantages
Ni-Cd batteries include:
· operation in a wide temperature range and resistance to temperature changes (for example, Ni-Cd batteries can be charged at negative temperatures, which makes them indispensable when working in the Far North, which is not particularly relevant in our latitudes); · they can deliver significantly more current to the load than other types of batteries; · resistance to high charge and discharge currents; · easily restored after long-term storage.
· the presence of a memory effect - if you regularly charge an incompletely discharged battery, its capacity will decrease due to the growth of crystals on the surface of the plates and other physical and chemical processes; · Cadmium is a very toxic substance, so the production of Ni-Cd batteries has a bad impact on the environment. There are also problems with recycling and disposal of the batteries themselves; · low specific capacity - the amount of energy that a fully charged battery should have. It is customary to express ampere hours (Ah); · large weight and dimensions compared to other types of batteries with the same capacity; · high self-discharge (after charging, up to 10% is lost in the first 24 hours of operation, and up to 20% of stored energy is lost in a month).
To the main advantages
Li-Ion batteries include:
· at least 2 times higher specific capacity;
· very low self-discharge; · no memory effect; · possibility of recharging at any time; · a large number of charge-discharge cycles (with proper operation they can withstand more than 2000 cycles); · environmentally friendly production and safety in operation.
· susceptible to aging; · low stability when working at low temperatures; · require the use of only the original charger; · high price.
However, if we still return to the choice of a screwdriver, then our preference is clearly for the Bosch GSR 10.8-2 Cordless Screwdriver, because it has significantly smaller dimensions, greater torque and is equipped with a modern and easy-to-use battery. But this is only our opinion, and the final decision is always yours.
Source: isell.by
Operating rules
As NiCd batteries operate, some changes occur in them, resulting in a gradual deterioration in performance characteristics, which ultimately leads to loss of performance.
Here is a list of these negative transformations:
- the useful area and mass of the electrodes are reduced;
- the volume of electrolyte and its composition changes;
- separators and organic impurities disintegrate;
- water and oxygen are lost;
- Leaks associated with the growth of cadmium dendrites on the plates manifest themselves.
In order to minimize the negative consequences for a nickel-cadmium storage device that arise during its storage and operation, it is necessary to neutralize the adverse effects on the battery:
⛔ if you subject the battery to heavy overcharging on a regular basis, then you can expect the following troubles: overheating, increased gas formation, loss of water in the electrolyte, destruction of electrodes, especially the anode, destruction of separators;
⛔ undercharging, leading to accelerated battery depletion;
⛔ prolonged operation at very low negative temperatures entails a change in the composition and volume of the electrolyte, an increase in the internal resistance of the drive, a decrease in its operational characteristics, specifically, the capacity decreases.
Fast charging with high current and significant degradation of the cadmium cathode lead to a significant increase in pressure inside the battery. As a result, excess hydrogen may be released in the electronic storage device, which entails an additional sharp increase in pressure, which can deform the body of the nickel-cadmium battery, disrupt the assembly density, increase internal resistance and reduce the operating voltage.
In units equipped with an emergency pressure relief valve, the risk of deformation can be reduced to zero, but irreversible changes in the chemical composition of the energy source cannot be avoided.
Nickel-cadmium can be charged with a current of 10% of its capacity for 14-16 hours. The most optimal discharge option would be to use a current equal to 20% of the storage capacity.
Recovery
Ni-Cd in case of loss of capacity can be restored almost completely. It will be necessary to organize a full discharge (up to 1 V per element) and subsequent charging in standard mode. This procedure can be done several times, this will ensure the most complete regeneration of the container.
Recovery can also be achieved through exposure to short current pulses for several seconds. Their value should be tens of times greater than the capacity of the drive being restored. Such manipulations will eliminate the internal short circuit in the battery components caused by the growth of dendrites. There are special industrial activators that produce the described effect.
One hundred percent restoration of the original capacity of nickel-cadmium batteries is impossible, since irreversible changes in the composition and properties of the electrolyte occur, as well as degradation of the plates. But you can extend the life of this equipment.
To carry out restoration measures at home, you will need to take the following steps:
1. We take a wire with a cross-section of at least 1.5 mm2 and connect the “-” of the device being restored to the cathode of a powerful electronic storage device. For example, you can take the battery from a car or from UPS.
2. We connect the second wire to the “+” of one of the batteries.
3. For 3-4 seconds, quickly touch the free “+” terminal with the free end of the second wire. The frequency of touches is 2-3 per second. During the entire process, do not allow the wires to “weld” at the connection points.
4. We use a voltmeter to measure the voltage on the recoverable battery; if it is absent, another recovery cycle is performed.
5. When electromotive force appears on the battery, it is placed on charging.
You can also try to organize the destruction of the dendrites in the electronic storage device by freezing them for two to three hours. Next you need to carry out intensive tapping. During the freezing process, dendrites become brittle and are destroyed by impact. Supposedly this will help get rid of them.
There are also more extreme methods for restoring NiCd batteries. For example, we drill out the body (only the outer shell) of the old element and, using a syringe, add distilled water there, which will gradually fill the voids. However, as a result, we will have big problems with the complete tightness of the power supply. Therefore, such recovery methods should be resorted to only in the most extreme cases, otherwise there is a chance of simply being poisoned by toxic substances in order to win several “bonus” work cycles.
Where are they used?
The main areas of application of Ni-Cd are equipment with increased discharge currents. For such electrical equipment, NiCd drives can provide stable power. They also do not overheat during operation at maximum current.
Ni-Cd serves a variety of transport: trolleybuses, small water vehicles, electric cars.
Before lithium energy sources entered the market, cadmium batteries were widely used to service portable tools, and also, in a flat design, were introduced into PCs to power independent memory. NiCd has also found its place in cameras, flashlights, calculators, and devices for improving hearing.
Nickel-cadmium can be stored for a long time in a discharged state and is not subject to the harmful effects of negative temperatures. Low internal resistance and low specific gravity make nickel-cadmium a very suitable option for powering the on-board power supply of aircraft and for servicing portable radio stations.
Now, due to stricter environmental requirements, most electric batteries of popular sizes, such as AA, AAA and others, are produced using Li-Ion and Ni-Mh technologies. But at the same time, quite a large number of nickel-cadmium batteries of various sizes, produced several years ago, are being safely used to this day. Naturally, now they can also be purchased, and for a rather attractive amount.
Types of drives
Most often, electric screwdrivers have a nickel-cadmium or lithium-ion battery. There are also Ni-Mg drives, which have their own advantages.
However, nickel-metal hydride batteries are rarely installed in screwdrivers, because the electrolytes heat up too quickly when charging. This is also very noticeable when working continuously with the tool.
Benefits of Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries
If you do not take into account the tendency to become very hot, Ni-Mg batteries have the following advantages:
- cause less damage to nature;
- less memory effect than others.
However, they are not able to compete with Ni-Kd and Ni-Li batteries. Therefore, batteries are not recommended due to their low efficiency.
Advantages of nickel-cadmium batteries
People criticize cadmium storage batteries because they are older. However, despite the numerous condemnations, these blocks have high performance. For example, they are more capacious and do not heat up as much during operation as the same nickel metal hydride battery cells.
This happens due to the heat-absorbing reactions that occur inside the battery. Heat absorption reaction is the absorption of generated heat inside an element. Such reactions do not release heat beyond the working mixture.
If you choose a battery cell for an electric screwdriver based on its practicality and productivity, then Ni-Cd is much better than Ni-Mh. Currently, they are the most common type of battery not only for electric screwdrivers or drills, but also for other household appliances.
Advantages of NI-CD batteries:
- Lower chance of overheating of block elements.
- They will not burn out or deteriorate in a short time, unlike Ni-Mg.
- Equipped with a durable and reliable metal casing, which provides good sealing of the structure.
- Resistant to various undesirable chemical reactions.
- Resistant to negative temperatures. They function even at -35°C.
- When used correctly, batteries last about 7-11 years.
- Adequate cost. Li Ion storage batteries cost much more.
First of all, remember that nickel batteries are not afraid of a complete discharge of the elements. Therefore, when working, discharge the storage unit to the very end.
After discharging, you can put the battery on charge, because it will not lose its capacity.
It is recommended to store batteries in a discharged state, because the reversible loss of capacity, or the so-called “memory effect,” will be less pronounced.
There is no need to recharge the battery during storage. Reversible loss of capacity is not a significant threat to the battery. To reduce damage from the “memory effect”, it is recommended to fully charge and discharge the battery several times. These manipulations will help reduce reversible loss of capacity.
Benefits of lithium-ion batteries
Compared to nickel-cadmium batteries, the Li Ion type of battery was invented relatively recently - in the 90s of the 20th century. In the beginning, this type of battery was dangerous due to the high risk of rupture. This was due to technical deficiencies.
Currently, most lithium-ion batteries are equipped with special sensors to monitor the heating of the elements and the charge level.
What are the advantages of Li Ion batteries? Comparing them with nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, one can notice that they have the following advantages:
- Can be used for a longer period of time thanks to its high capacity.
- No reversible loss of capacity (as stated by 99% of Li Ion battery manufacturers and sellers).
- A lithium battery pack has much less weight with the same capacity than a cadmium battery.
Lithium batteries have a number of disadvantages. For example, they are more sensitive to even the smallest voltage surges during charging.
In contrast to cadmium, lithium-ion is more sensitive to low temperatures, especially when leaving a warm room outside in cold weather.
Of course, any type of battery is more or less sensitive to sudden temperature changes, but knowledgeable experts say that lithium-ion batteries are the most demanding.
Lithium-ion batteries lose their declared capacity faster if they are not used for a long time. Their service life is no more than two or two and a half years.