Hexagonal (hexagonal) shanks
The shank of such a drill can be clamped either with a regular three-jaw chuck or (if the size of the shank allows it) inserted into a regular 1/4-inch bit holder (this speeds up drill replacement). The companies Festool and Protool produce drills with a special type of hex shank - similar in geometric dimensions, but with slightly rounded edges (Centrotec drills). This drill can be inserted into either a Centrotec holder or a regular holder, but regular drills do not fit into a Centrotec holder. Using Centrotec drills reduces the common disadvantage of hex shank drills - less accuracy when using a 1/4" holder rather than a jaw chuck. With a shank of this type (although not necessarily corresponding to the 1/4-inch size), not only twist drills, but also feather drills, Fostner drills, etc. are produced.
SDS-plus
The most common type of shank with a diameter of 10 mm, which is inserted 40 mm into the hammer drill chuck. It has four grooves (two open for guide wedges and two closed for fixation with locking balls). The contact area of the wedges is 75 mm2. Drills with such a shank are used on light construction hammer drills; the minimum length of drills with such a shank is about 110 mm and the maximum is 1000 mm. The diameter of the drill is usually from 4 to 15 mm (the most common diameters are 6, 8, 10 and 12 mm).
Types and scope of application of SDS cartridges
Depending on the diameter of the shank with which the tool or adapter is equipped for fixing it on the hammer drill, SDS chucks are divided into five main types: regular SDS chucks, models of the SDS-top, SDS-quick categories, as well as SDS-plus and SDS-chucks. max. The most popular are the SDS-plus category chucks, which are designed to hold tools with a shank diameter of 10 mm. The shank of the tool, adapted for fixing devices of the SDS-plus category, enters them to a depth of 40 mm. In this case, the diameter of the working part of the tool, which is fixed in SDS-plus chucks, can be in the range of 4–26 mm.
Read also: Do-it-yourself temperature regulator for a soldering iron
The maximum tool length that can be clamped in SDS-plus chucks is 1 meter, and its most common working diameters are in the range of 6–12 mm. Devices designed to hold SDS-plus shanks and corresponding adapters for rotary hammers in them are used to equip light and medium category equipment, the weight of which, excluding the weight of the tool, ranges from 3 to 5 kg. It is precisely these hammer drills, which are designed for impact loads of up to 5 J, that are most popular among home craftsmen and small repair teams.
Common types of SDS shanks
SDS-max chucks, with a bore diameter of 18 mm, are used to equip heavy professional rotary hammers, whose weight starts from 5 kg. Such hammer drills, which can be used in conjunction with tools with a working diameter of up to 6 mm, are able to create an impact load of up to 30 J. To ensure accurate and reliable fixation of the tool in such serious equipment, an additional guide groove is provided on shanks of the SDS-max category .
SDS-top and SDS-quick chucks are intermediate options for equipping rotary hammers and are used much less frequently than the models described above. Meanwhile, the design of SDS-quick devices, which were developed by Bosch engineers in 2008, is worth a closer look. The tool is inserted into the SDS-quick series chucks not using grooves, but through protrusions on the shank. The design features of SDS-quick chucks allow them to hold tools with a hexagonal shank and a quarter-inch size.
The SDS-quick system is used in Bosch UNEO cordless hammer drills
Drills with conical shank (including Morse taper)
Mainly used in industrial hand tools and machine tools. Depending on their purpose, drills can be divided into drills for metal, concrete, wood, as well as drills for glass and tiles.
Drills for metal work are the most versatile; they can be used to make holes in wood, metal, and plastic. Such drills have a screw shape with a pointed end. Standard metal-cutting drills have a point angle of 120°. The most common are twist drills. They have two main cutting edges formed by the intersection of the front helical surfaces of the drill flutes, along which chips flow, with the rear surfaces facing the cutting surface, as well as a transverse cutting edge (jumper), formed by the intersection of both rear surfaces, and two auxiliary cutting edges, formed by the intersection of the front surfaces with the surface of the ribbon. Twist drill sizes are standardized. The main size of a drill is considered to be the diameter. Therefore, when drilling, select hole sizes for which there is a corresponding drill diameter.
Drills are divided into several sizes based on their length. There are groups of drills with an extended shank, and some with a shortened one. In drills with a cylindrical shank, the length of the working part of the drill depends on the diameter, and is usually equal to 50 mm plus the diameter of the drill. Over time, the drill wears out and requires sharpening. This can be determined by the following signs: - the drill slowly plunges into the material being processed and becomes very hot, - drilling is accompanied by a squealing sound, - the drilled holes have a rough surface. Drills with dull cutting edges with a diameter of up to 12 mm are sharpened by hand. Drills of larger diameter are sharpened on universal and special sharpening machines using a special device.
Important parameters
Without drilling holes in various surfaces, construction and repairs are impossible. And if a regular electric drill is quite suitable for making holes in a structure made of wood materials, brick and plasterboard, then only a hammer drill can cope with a concrete structure. The peculiarity of this equipment is that it can not only drill the surface being processed, but also exert an impact load on it, that is, perform the function of a jackhammer. Naturally, to install it on a hammer drill you need to use a special tool - a drill. It differs from a conventional metal drill in a number of parameters.
The drills differ from each other in their design features, among which the following should be highlighted:
- design of the spiral part;
- the presence of a special cavity in the inner part;
- material for manufacturing the working part, which can be a hard alloy;
- number and geometric parameters of cutting edges.
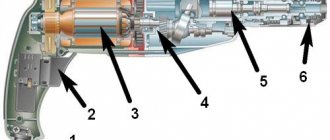
Main parts of the drill
Drills are also distinguished from ordinary drills by the design of the shank, which allows them to be securely fixed in the chuck of the equipment used. The most common types of concrete drill shanks and chucks used when working with rotary hammers are the following.
SDS+
SDS-plus drills, like cartridges in this category, are designed for installation on medium and light series rotary hammers. It is devices of this type that are most often used by home craftsmen to perform various repair and construction work. The diameter of the SDS-plus shank cannot exceed 18 mm.
Drills with this shank are designed for light construction hammer drills
SDS-max
Intended for concrete processing, drills with shanks of the SDS-max category (the diameter of their fastening part exceeds 18 mm) are used in the configuration of professional series rotary hammers.
The SDS-max system with an increased contact area of the wedges is designed for heavy hammer drills
The main manufacturers of SDS-plus concrete drills (the most popular category) are Chinese companies. As a rule, the parameters of such products comply with the requirements set by GOST, so they can be installed on any rotary hammers. Meanwhile, you should not try to insert a tool for working with concrete into a regular drill, since it will not be possible to do this even with considerable effort.
To choose the right drill for a hammer drill, you should take into account such parameters of the working part as:
- length, the size of which determines how deep the hole you can drill;
- diameter.
Operating parameters of the drill
Taking into account the fact that hammer drills are used to work with particularly durable materials (concrete, natural and artificial stone), their design has a reinforced design, and the working part is made in the form of a double spiral. This is what allows you to use hammer drills when working with concrete and other materials for a long time, without worrying about their technical condition. Many models of concrete drills for rotary hammers are equipped with a tip made of the strongest alloy of the VK8 brand, which allows them to be successfully used for processing materials of particularly high strength.
Selecting tools of this type is not difficult: all of their most significant parameters are indicated in the labeling. For example, if in front of you is a concrete drill marked 6x160, this means that it has the following dimensions: working diameter - 6 mm, length - 160 mm. It must be borne in mind that the marking of the tool indicates its working length, which is slightly smaller than the dimensions of the working part.
The diameter of the working part of concrete drills installed on a hammer drill can be in the range of 4–30 mm. The most popular sizes fall in the range of 6–10 mm. Using a concrete drill of this size, you can, in particular, make a hole for placing a dowel.
Drill for concrete, granite, stone
Concrete is one of the most stubborn materials. It must be drilled using drills with specially welded carbide plates, or, as we call them, Pobedit drills. The first carbide material, created in the USSR in 1929 based on a composite of tungsten carbide and cobalt, bore the proud name “Pobedit”. This name has become a household name, and drills with any carbide tips are called pobedit by inertia. Pobedit drills are sold ready for use.
For drilling wood, chipboard, soft and hard plastics, an ordinary drill made of high-strength steel (a simple piece of hardware without any bells and whistles) is suitable. In principle, you can drill a small-diameter hole in wood or plastic with an ordinary nail by inserting it into a drill, but the variety of tasks dictates its own requirements, and today on store shelves there are wood drills that vary in purpose and design. These are twist drills, feather drills, and annular drills.
Twist drills for wood are usually used for drilling small holes. And they are produced with diameters from 8 to 28mm with three series of lengths 300mm, 460mm, 600mm. Feather drills for wood are most often produced with a diameter of 10mm. This type of drill is convenient for drilling blind holes in chipboard, as well as when using an extension for drilling deep holes. Feather drills are produced in various diameters, the most common are 10,12,16,18, 20, 22, 25mm.
Hole drills for wood are sold in sets and are a universal holder with a set of interchangeable bits. Used as drill attachments. They are used when it is necessary to drill a hole of large diameter: for 25-50mm furniture pipes, 80, 90 and 120mm fans, 60mm glasses for built-in switches or sockets. The kit also includes a pilot drill and a hex key. For glass, a diamond drill is used (a drill with diamond dust chips sprayed onto the tip). It is characterized by a precisely ground cutting plate made of hard metals in the shape of a peak. Ensures precise drilling of holes even in the most fragile materials. Has a cylindrical shank for mounting in a drill chuck. Used for drilling glass, fiberglass, mirrors, bottles, ceramics, porcelain, etc. This type of drill can be resharpened many times.
Drill SDS
A drill is a cutting tool for making holes in solid materials - concrete, stone, brick. In everyday life and construction it is the main type of equipment for a rotary hammer.
Structurally similar to a drill, it has a shank and a spiral for removing permitted material from the drilling zone (very rarely, a cavity inside the drill is used for this purpose in combination with a vacuum dust removal system). The cutting part of the drill is made of carbide and can have different sharpening configurations and a different number of cutting edges. To increase durability, the cutting edge is made not sharp, like a drill, but slightly rounded. Unlike a drill, the drill has special elements on the shank for mounting in the hammer drill chuck (notches or protrusions). The main purpose is hammer drilling (therefore, the drill is not used for drilling fragile materials). Application material: concrete. Drilling bricks with a drill is not always economically justified, and sometimes technologically unacceptable, in particular when drilling holes for an anchor or dowel in a hollow brick.
How do chucks for hammer drills work?
To effectively use different hammer drill bits, you need to ensure that they are securely attached. A special cartridge is used for this. Its first models began to be developed back in the 30s of the last century, when hammer drills appeared on the market, the mass production of which was mastered by the world famous company Bosch.
Read also: Homemade extruder for feed
Such a manual device as a hammer drill was almost immediately appreciated by consumers, since it can be used to combine drilling with pulse chiselling, which significantly increases the efficiency of the processing performed. The main drawback of the first models of rotary hammers was precisely due to the fact that the weakest link in their design was the cartridge, which quickly became unusable under the influence of shock loads.
As a result of long-term development, manufacturers of hammer drills and chucks have come to the following conclusion: the simpler the design of the clamping device, the more reliable it is in operation.
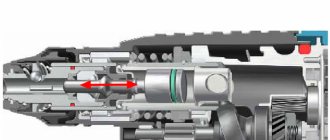
Externally, the hammer chuck is a completely closed clamping device
As a result, three main types of cartridges for rotary hammers were created, which in turn are divided into subtypes.
There are chucks in which the working attachment is fixed using a special key that activates cams that reliably clamp the shank of the tool being used. The most significant advantage of this type of chucks is that they provide reliable fastening of the tool used in conjunction with the hammer drill. Meanwhile, to replace the working tool in such a chuck for a hammer drill, you will need to spend significantly more time than when using other types of clamping devices.
Main types of hammer drill chucks
The working attachment of the hammer drill can also be fixed on it using a quick-release chuck (KLC), which is activated only by the force created by the operator’s hands. Depending on the design, cartridges of this type can be single- or double-clutch, the operating principles of which also differ.
Single-socket chucks are easier to use, but they can only be used in conjunction with drills that have the ability to automatically lock the working shaft. To activate such a cartridge, the effort of one hand is sufficient. To use a double clutch clamp, you need to hold the rear clutch with one hand and rotate the front clutch with the other.
Features of application
The drill, unlike the drill, must move freely with a certain amplitude along its axis in the hammer drill chuck (for example, the SDS+ drill moves approximately 1 cm). Before fixing it in the chuck, a special lubricant is applied to the drill shank to reduce power losses and increase the service life of the drill and chuck. Some types of drills: A - for metal processing; B - for wood processing; C - for concrete processing; D—feather drill for woodworking; E - universal drill for processing metal or concrete; F - for sheet metal processing; G is a universal drill for working metal, wood or plastic. Tail parts: 1, 2 - cylindrical; 3 - SDS-plus; 4 - hexagon; 5 - tetrahedron; 6 - trihedron.
Need some advice? Request a call! Send a request for fasteners
07.12.2010
About attachments for rotary hammers
Theoretically, a tool with a shank for SDS-plus chucks and even a tool with an even smaller seat diameter can be installed on a hammer drill chuck of the SDS-max category. To solve this problem, a special attachment (adapter) is used, which today can be purchased on almost any construction market. Meanwhile, it is strictly not recommended to use such adapters for a rotary hammer, since using a tool of a smaller diameter on heavy-duty rotary hammers will quickly render it unusable.
As a rule, tools for rotary hammers are sold immediately in packages and cannot be restored after failure. However, it should not be confused with conventional drills, which differ from it in the shape of the sharpening and the structure of the spiral.
The first and one of the most important stages for carrying out high-quality repair work is the correct choice of construction tools. When it is necessary to carry out extensive repairs, deal with brickwork or even reinforced concrete, then you cannot do without a powerful hammer drill. To choose the right hammer drill, you should consider that they come in three types: light, medium and heavy. Each of them differs in size, impact force, as well as the types of shanks used on the cartridge, which are SDS plus and SDS max. What is better and what are the design differences between them, we will discuss in this article. Perhaps we should note that there is a type of chuck shanks called SDS-top, designed for medium-sized drills, but their distribution is minimal and almost completely replaced by drills with an SDS plus shank.