Screwdriver speed controller
An electric screwdriver operates either from a 220 V network or from a rechargeable battery. Its power depends on the battery voltage. The screwdriver rotation speed starts at 15,000 rpm. In addition, a powered screwdriver has 2 rotation speeds: a slower one for screwing, a higher one for drilling. The speed control is located inside the power button. The rather miniature size of this tool assembly is achieved using microfilm technology. Its main part is a triac. The operating principle of the regulator is as follows:
- When the button is turned on, an alternating current having a sinusoidal phase is supplied to the control electrode of the triac.
- The triac opens and current begins to pass through the load.
The response time of the triac depends on the amplitude of the control voltage. The greater the amplitude, the earlier the triac is triggered. The amplitude value is set using a variable resistor connected to the start button. The button connection diagram differs in different models. It is possible to connect a capacitor to the speed controller.
Often, in the current economic conditions, the buyer cannot always afford a full-fledged expensive screwdriver from reputable companies. Cheaper models may not have this feature. But this is no reason to despair. You can assemble the speed controller yourself, which we will talk about below.
The screwdriver speed controller is assembled on the basis of a PWM controller and a key multi-channel field-effect transistor. The operation of this tool unit is controlled by a resistor. Its position depends on the pressure on the screwdriver start button.
The direction of rotation of the working body changes by changing the poles of the voltage that is supplied to the motor brushes. This is done instrumentally using changeover contacts actuated by a reverse lever.
It is possible to assemble such a regulator with your own hands. We will look at how to do this below.
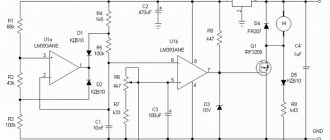
A diagram of the elements that make up the speed controller is shown in the figure below.
In this case, a dual comparator microcircuit LM 393 is used. Here, the first comparator works as a sawtooth voltage generator, and the second one is PWM. The control signal for PWM is the voltage drop across the motor contacts. To put it simply, in the diagram the electric motor looks like active and inductive resistances connected in series with each other. When the load changes, the ratio of these resistances changes accordingly, the regulator controls this and changes the PWM filling, thereby stabilizing the speed.
An electronic transformer should be used as the power source for PWM. It is a half-bridge voltage converter from 220 to 12 V, which is used to power halogen lighting lamps. Its dimensions are comparable to the size of a matchbox. The price fluctuates between 2–3 USD. e. It is necessary to add a rectifier to the output (these are four diodes, for example, KD 213), as well as a capacitor with a capacity of several thousand microfarads at 25 volts. All this will constitute a switching power supply with a constant output voltage.
We should also talk about making a printed circuit board for the regulator. To make it you need a sheet of photo paper and a laser printer. First you need to print the design on photo paper using a laser printer, then transfer it to the board blank using a heated iron. The board blank with the paper attached is placed in a container and placed under a stream of hot water. This is done so that the gelatin layer of the photo paper swells and it peels off from the board. The remaining pattern on the board is etched with ferric chloride.
Adjusting the speed of the commutator motor without loss of power. Device
The commutator motor usually consists of a rotor (armature), stator, brushes and tachogenerator:
- The rotor is the rotating part, the stator is the outer magnet.
- Brushes made of graphite are the main part of the sliding contacts, through which voltage is applied to the rotating armature.
- A tachogenerator is a device that tracks the properties of rotation. In the event of a violation of the uniformity of movement, it corrects the voltage entering the engine, thereby making it smoother.
- The stator may contain not one magnet, but, for example, 2 (2 pairs of poles). Also, instead of static magnets, electromagnet coils can be used here. Such a motor can operate on either constant or alternating current.
The ease of adjusting the speed of the commutator motor is determined by the fact that the rotation speed directly depends on the magnitude of the applied voltage.
READ How to Drill Concrete with an Impact Drill
Apart from this, a fundamental feature is that the rotation axis can be directly connected to a rotating tool without the use of intermediate devices.
If we talk about their systematization, then we can talk about:
- Constant current collector motors.
- AC commutator motors.
In this case, we are talking about the specific current that powers the electric motors.
The difference lies in how these connections are organized.
Here it is customary to distinguish:
- Parallel excitation.
- Consistent excitation.
- Parallel-sequential excitation.
Screwdriver force regulator
The force regulator is a clutch that limits the force when the chuck rotates. It is made in the form of a rotating plastic drum. The amount of tightening is adjusted using a digital scale located around the circumference of the drum. By increasing the tightening value, you screw the screw in deeper.
This function will be necessary when working with material products of varying degrees of hardness, since when working with soft material, the body of the self-tapping screw will be easily recessed into it; too high a hardness of the material will contribute to the violation of the geometry of the screw, especially if it is small in size. The ratchet, as the regulator is also called, prevents cutting off the splines of the screws, as well as wear on the screwdriver attachments. The adjusting ring should be tightened in stages, starting with the slightest force. In those screwdrivers in which drilling can be done, the last pictogram on the ring will be in the form of a drill. In this position, maximum torque is achieved.
Electronic screwdriver speed control
The rotation speed of the screwdriver attachment can be adjusted mechanically or automatically. Automatic speed control occurs using a processor. You can set the desired operating parameters using the speed selection toggle switch. It is located on top of the body. In many models, speed control is realized through the start button. The stronger the finger pressure on it, the higher the speed will be.
After reading this article, you received information on how to assemble a screwdriver speed controller with your own hands, became familiar with the design of the force regulator, and understood the function of electronic adjustment of the tool. We hope you found the article useful.
Source: pro-instrument.com
Communities › Electronic Crafts › Blog › My micro drill and automatic speed controller.
Good day to everyone reading this post! Prologue
.
I understand that most of the participants in this community are seasoned “electronic” wolves, but suddenly my post will still be useful to someone...
Recently I have become a little interested in radio electronics, not least because of the appearance of the car. Having made a couple of printed circuit boards to control the battery charge (one, two), I realized that I no longer wanted to drill millimeter holes with a screwdriver. And I began to study the hardware on the topic of microdrills for printed circuit boards. I re-read a bunch of forums, watched gigabytes of videos and went into the bins. And in the bins they found a power supply from an inkjet printer (24V/1A) that had served faithfully for ten years and two motors from it labeled QK1-0889. No matter how hard I searched, I still couldn’t find the exact datasheet for this motor. But it spins very quickly from this power supply. I measured the shaft (2.3 mm) and ordered a collet chuck with a set of collets on AliExpress. While the kit was on the way, I continued to learn the intricacies of drilling printed circuit boards. And so, I came across an automatic speed controller. I will say right away that there are a great variety of regulators for microdrills. I decided to go from simple to complex.
Drill speed controller diagram
All modern drills are produced with engine speed regulators built into them, but for sure, in the arsenal of every radio amateur there is an old Soviet drill, in which the change in speed was not intended, which sharply reduces the performance characteristics.
Speed controller circuit for a Soviet drill
The figure below shows a diagram of a speed controller for an electric drill motor, assembled as a separate external unit and suitable for any drills with a power of up to 1.8 kW, as well as for other similar devices that use a commutator AC motor, for example, in grinders. The regulator parts in the diagram are selected for a typical drill with a power of about 270 W, 650 rpm, voltage 220V.
The thyristor type KU202N is mounted on a radiator for the purpose of its normal cooling. To set the desired rotation speed of the electric motor, the regulator cord is connected to a 220 V power outlet, and the drill is plugged into it. Then, by moving the variable resistance knob R, set the required speed for the old drill.
Angler speed controller circuit diagram
The presented circuit is simple enough to be repeated even by a novice radio amateur. The components and parts required for assembly are cheap and easily available. It is recommended to assemble the structure in a separate box with a socket. Such a device can be used as a portable device with a standard power regulator
Speed regulator of a homemade micro drill
The operating principle of this amateur radio homemade product is as follows: when the load is small, the current flows small, and as soon as the load increases, the speed gradually increases.
The LM317 microassembly must be installed on the radiator. 1N4007 diodes can be replaced with similar ones designed for a current of at least 1A. The printed circuit board is made on single-sided fiberglass. Resistance R5 with a power of at least 2W, or wire.
The 12V power supply should have a small current reserve. Using resistor R1 we set the required idle speed. Resistance R2 is necessary to set the sensitivity to the load; it sets the required torque for increasing the speed of the microdrill. If you increase the capacity of C4, the high speed delay time increases.
Micro Drill Speed Controller for Drilling Small Holes in PCBs
The circuit presented below allows you to assemble a very simple, cheap and useful speed controller for a 12-volt microdrill for drilling holes in printed circuit boards in amateur radio practice.
The LM555 microassembly is used as a pulse width modulator. The supply voltage for PWM is reduced and stabilized using the LM7805 chip). Precision tuning resistor P1 of 50 KOhm allows you to adjust the rotation speed of the drill. The IRL530N field-effect transistor is used as an output drive element and can switch current up to 27A. In addition, it has fast switching times and low resistance. The 1N4007 diode is needed to protect against counter EMF. As an alternative, you can take the MBR1645 Schottky diode.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) used in this design is an effective method of varying speed and power for all DC motors.
DIY drill repair
> Tools > DIY drill repair
An electric drill is now present in the tool kit of almost any craftsman, as it is an indispensable unit in everyday life or in the professional field.
But, like any part, a drill can break, and in order not to contact specialists every time, you need to be able to maintain and repair your tool yourself.
This article discusses signs of breakdown and options for eliminating them, as well as the most common malfunctions and how to repair a drill with your own hands.
Drill device
A drill is an electric tool and performs the functions of drilling holes in various materials, as well as tightening screws. The work is carried out using special drills and tips that are inserted into the chuck.
An electric drill is equipped with a motor driven by a current of 220 Volts, which rotates the transmission gears and other components.
The power of the power unit is adjusted by a special regulator, which is located on the start button and turns in both directions.
Some models are equipped with a rotation axis switch, which changes the location of the brushes; from its drill chuck, the drill chuck can rotate both to the right and to the left.
There are two types of chuck: with a splined part and with a smooth part. In the first case, the drill is clamped with a special key, which, when turned, twists the lower part of the head and fixes the part. A regular smooth chuck can only be tightened by hand, so if you need to tighten the drill tightly, a chuck with splines has an advantage.
Main types of electric drill malfunction
DIY LED lamp repair
Any tool can suddenly break down, this happens due to improper use, violation of maintenance regulations, or simply careless attitude towards equipment. In order to prevent breakdowns, you must follow all the rules established by the manufacturer, as well as timely repair and replace worn-out parts.
There are several types of possible malfunctions of a household electric drill, which include:
- When the start button is pressed, the drill does not operate. First of all, in this case it is necessary to check the quality of the contact between the plug and the socket, as well as the presence of electricity. Most often, such a malfunction occurs due to burnt contacts inside the plug or in the cord itself, when a wire break occurs as a result of a load or a change in current. This problem can be solved by simply replacing the lead cable;
- The drill chuck rotates, but the speed remains unchanged. Here we can assume that the drill speed controller is faulty, which may break due to mechanical deformation or dirt getting on the roller. There is a built-in contactor inside the regulator that can burn out, and it can only be repaired by replacing the entire assembly, since soldering such a small part at home will not work. In general, in a drill with a speed control mechanism, this is the most vulnerable part, so it must be treated with the utmost responsibility;
- When starting, an unpleasant burning smell appears from the brush vent, and the engine rotor sparks. The first thing you need to do is turn off the device and unplug the cord from the outlet, otherwise it will be much more difficult to repair the electric drill. Next, you need to carefully inspect the engine, determine the level of wear of the brushes and the rotor itself, and also check whether there are foreign objects or other contaminants inside that interfere with the rotation of the rod;
- Crunching sound in the central part of the instrument. All mechanisms and gears are hidden behind a plastic case, so you won’t be able to immediately identify the broken part. Most often, the splines of the drive disk break, especially in a drill with a hammer drill function, which, in addition to the usual transmission, has an impact mechanism and a locking device. To replace these elements, you will need to completely disassemble the instrument and carry out a detailed troubleshooting. It is important not to use a broken drill, since broken pieces can fall into other components, which, when rotated, will completely destroy the mechanism, and it will not be possible to restore it;
Rotation transmission mechanism
- The chuck does not secure the drill, the clamping blades do not converge when tightened with a wrench. Most often, this malfunction can be eliminated very quickly; the chuck itself is attached to the drill body with an ordinary screw, the head of which is located inside the head and can be unscrewed due to vibration. As a result, the bolt prevents the petals from tightening the drill; it must be tightened by inserting a shaped screwdriver;
- On an impact drill, the drill is inserted into a special chuck equipped with a quick-release mechanism; often pieces of metal or concrete get inside this unit, which get clogged into small cracks and do not allow the latch to fit into its socket, so the inserted chuck constantly pops out of the hole. Detailed cleaning of the instrument and removal of all contaminants will help here.
These malfunctions are the most common and often occur when using an electric drill at home. If more serious breakdowns occur, to restore the tool without errors, it is better to contact a service center, since without some experience and repair instructions it will not be possible to fix the breakdown.
Self-cleaning brushes and replacing them
During operation, especially in difficult conditions, plaque forms on the brushes, and the electric drill begins to heat up and spark. To repair a drill with your own hands, by replacing the brushes with new ones, you need to follow a certain algorithm of actions.
The first step is to unscrew the screws at the back of the electric motor.
Most tool manufacturers, for ease of service, make this part in such a way that it can be quickly removed without disassembling the main body, and the start button remains in place. After unscrewing the cover, it is completely removed, making the motor brushes and its rotor accessible for maintenance.
Next, you need to disconnect the wire terminals from the carbon brushes and, bending the locking tabs, pull the element out. The power unit is equipped with two brushes on both sides, which wear out simultaneously and therefore must be replaced together.
By the level of tip wear, you can understand the condition of the rotor bearings.
If the wear is located in the upper or lower corner of the carbon rectangle, then we can conclude that there is play in the motor armature bearing; this part must also be replaced.
Before installing new drill brushes, you need to blow all internal elements with compressed air; this will help clean the rotor of dust and prevent the formation of plaque on the new parts.
The button must also be cleaned so that its return spring can move freely.
The brushes are inserted into the seat and secured with a lock, after which the terminals are connected and the cover is reassembled.
If it is necessary to replace the start button or speed controller, then it is possible to repair this unit only if there is a connection diagram for the drill button, which must be indicated in the operating instructions for the tool. The connection of all electrical parts and cables must be carried out in a de-energized area and only in accordance with the diagram.
Thus, when planning to repair an electric drill yourself, you need to acquire special literature and tools so that there is no doubt about the quality of the electrical connections when installing new spare parts.
Source: https://elquanta.ru/instrument/remont-dreli-svoimi-rukami.html
PWM speed controller
Let's look at the first 5 amp PWM regulator. There is such a favorite microcircuit of all radio amateurs - this is the NE555 timer (or the Soviet analogue KR1006VI). It is on this chip that the PWM regulator is assembled. In addition to the timer, here I use a 9 volt stabilizer LM7809, a powerful N-channel field effect transistor IRF540, a dual Schottky diode, as well as other small parts. The circuit by which this regulator is assembled is known to everyone and is very popular.
The signet of this board can be downloaded - PWM 5A
In a more powerful design, I simply use parallel connection of several IRF540 field-effect transistors and a more powerful dual Schottky diode. Otherwise everything is the same.
The signet for this board can be downloaded - PWM 10A Connecting the PWM controller is very simple. You see 4 terminals - two terminals for power supply and , and two terminals for connecting the motor and . I also made a PWM controller with current protection. For these purposes, I used the common operational amplifier LM358 and two PC817 optocouplers. When the current that we set with trimmer R12 is exceeded, the trigger-latch on the op-amp DA3.1, optocouplers DA4 and DA5 is triggered and the generation of pulses on the 5th leg of the NE555 timer is blocked. To start generation again, you need to briefly remove power from the circuit using the S1 button.
The seal of this board can be downloaded - PWM 10A with protection. The PWM regulators are all operational, I checked their operation using a motor from a screwdriver. Made a video -
Excellent Youtube affiliate - https://join.air.io/roshansky
Source: i-perf.ru
The 555 timer is widely used in control devices, for example, in PWM speed controllers for DC motors.
Anyone who has ever used a cordless screwdriver has probably heard a squeaking sound coming from inside. This is the whistling of the motor windings under the influence of the pulse voltage generated by the PWM system.
It is simply indecent to regulate the speed of an engine connected to a battery in another way, although it is quite possible. For example, simply connect a powerful rheostat in series with the motor, or use an adjustable linear voltage regulator with a large radiator.
A variant of the PWM regulator based on the 555 timer is shown in Figure 1.
The circuit is quite simple and is based on a multivibrator, albeit converted into a pulse generator with an adjustable duty cycle, which depends on the ratio of the charge and discharge rates of capacitor C1.
The capacitor is charged through the circuit: +12V, R1, D1, the left side of the resistor P1, C1, GND. And the capacitor is discharged along the circuit: upper plate C1, right side of resistor P1, diode D2, pin 7 of the timer, bottom plate C1. By rotating the slider of resistor P1, you can change the ratio of the resistances of its left and right parts, and therefore the charging and discharging time of capacitor C1, and, as a consequence, the duty cycle of the pulses.
Figure 1. PWM circuit - regulator on a 555 timer
This scheme is so popular that it is already available in the form of a set, as shown in the following figures.
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of a set of PWM regulators.
Timing diagrams are also shown here, but, unfortunately, the part values are not shown. They can be seen in Figure 1, which is why it is shown here. Instead of bipolar transistor TR1, without altering the circuit, you can use a powerful field effect one, which will increase the load power.
By the way, another element has appeared in this diagram - diode D4. Its purpose is to prevent the discharge of the timing capacitor C1 through the power source and load - the motor. This ensures stabilization of the PWM frequency.
By the way, with the help of such circuits you can control not only the speed of a DC motor, but also simply an active load - an incandescent lamp or some kind of heating element.
Figure 3. Printed circuit board of a set of PWM regulators.
If you put in a little work, it is quite possible to recreate this using one of the programs for drawing printed circuit boards. Although, given the small number of parts, it will be easier to assemble one copy using a hinged installation.
Figure 4. Appearance of a set of PWM regulators.
True, the already assembled branded set looks quite nice.
Here, perhaps, someone will ask a question: “The load in these regulators is connected between +12V and the collector of the output transistor. But what about, for example, in a car, because everything there is already connected to the ground, the body, of the car?”
Yes, you can’t argue against the mass; here we can only recommend moving the transistor switch to the gap in the “positive” wire. A possible version of such a scheme is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 6 shows the MOSFET output stage separately. The drain of the transistor is connected to +12V of the battery, the gate simply “hangs” in the air (which is not recommended), a load is connected to the source circuit, in our case a light bulb. This figure is shown simply to explain how a MOSFET transistor works.
In order to open a MOSFET transistor, it is enough to apply a positive voltage to the gate relative to the source. In this case, the light bulb will light up at full intensity and will shine until the transistor is closed.
In this figure, the easiest way to turn off the transistor is to short-circuit the gate to the source. And such a manual closure is quite suitable for checking the transistor, but in a real circuit, especially a pulse circuit, you will have to add a few more details, as shown in Figure 5.
As mentioned above, an additional voltage source is required to turn on the MOSFET transistor. In our circuit, its role is played by capacitor C1, which is charged via the +12V circuit, R2, VD1, C1, LA1, GND.
To open transistor VT1, a positive voltage from a charged capacitor C2 must be applied to its gate. It is quite obvious that this will only happen when transistor VT2 is open. And this is only possible if the optocoupler transistor OP1 is closed. Then the positive voltage from the positive plate of capacitor C2 through resistors R4 and R1 will open transistor VT2.
At this moment, the input PWM signal must be at a low level and bypass the optocoupler LED (this LED switching is often called inverse), therefore, the optocoupler LED is off and the transistor is closed.
To turn off the output transistor, you need to connect its gate to the source. In our circuit, this will happen when transistor VT3 opens, and this requires that the output transistor of the optocoupler OP1 be open.
The PWM signal at this time is at a high level, so the LED is not shunted and emits the infrared rays assigned to it, the optocoupler transistor OP1 is open, which as a result turns off the load - the light bulb.
One of the options for using such a scheme in a car is daytime running lights. In this case, motorists claim to use high beam lamps turned on at full intensity. Most often, these designs are on a microcontroller; there are plenty of them on the Internet, but it’s easier to do it on an NE555 timer.
Source: electric.info
Article rating:
Save to:
Screwdriver speed controller diagram Link to main publication
Control principle
When the rotation speed of the motor shaft is set by a resistor in pin circuit 5, a sequence of pulses is formed at the output to unlock the triac by a certain angle. The speed of rotation is monitored by a tachogenerator, which occurs in digital format. The driver converts the acquired pulses into an analog voltage, which is why the shaft speed is stabilized at a single value, regardless of the load. If the voltage from the tachogenerator changes, the internal regulator will increase the level of the output control signal of the triac, which will lead to an increase in speed.
The microcircuit can control 2 linear accelerations, allowing you to achieve the dynamics required from the motor. One of them is installed on the Ramp 6 output of the circuit. This regulator is used by washing machine manufacturers themselves, so it has all the advantages to be used for domestic purposes. This is ensured by the presence of the following blocks:
- Voltage stabilizer to ensure normal operation of the control circuit. It is implemented at pins 9, 10.
- Rotation speed control circuit. Implemented using MS pins 4, 11, 12. If necessary, the controller can be switched to an analog sensor, then pins 8 and 12 are connected once.
- Starting impulse block. It is implemented at pins 1, 2, 13, 14, 15. It adjusts the duration of control pulses, delays, their formation from a constant voltage and calibration.
- Sawtooth voltage generation device. Conclusions 5, 6 and 7. It is used to regulate the speed according to this value.
- Control amplifier circuit. Conclusion 16. Allows you to adjust the difference between the given and actual speed.
- Current limiting device at pin 3. When the voltage on it increases, the triggering angle of the triac decreases.
The introduction of a similar circuit provides real control of the commutator motor in all modes. Thanks to forced acceleration control, it is possible to achieve the desired acceleration speed up to a given rotation speed. Such a regulator can be used for all modern washing machine motors used for other purposes.
Crash test of speed control board
The board for adjusting the speed of commutator electric motors on the TDA1085 microcircuit allows you to control the engines without loss of power. An indispensable condition for all this is the presence of a tachometer (tachogenerator) on the electric motor, which allows for feedback from the motor to the control board, and specifically to the microcircuit. In more ordinary language, which would be clear to everyone, approximately the following happens. The motor rotates at a certain number of revolutions, and a tachometer installed on the electric motor shaft records these readings. If you start to load the engine, the shaft speed will naturally begin to drop, which will also be recorded by the tachometer. Now let's look further. The signal from this tachometer goes to the microcircuit, it sees this and gives a command to the power elements to add voltage to the electric motor. Thus, when you pressed the shaft (apply a load), the board automatically added voltage and the power on this shaft increased. And on the contrary, let go of the motor shaft (the load was removed from it), she saw this and reduced the voltage. Thus, the speed does not remain low, but the moment of force (torque) remains unchanged. And the most important thing is that you can adjust the rotor speed in a wide range, which is very convenient in the use and design of various devices. That’s why this product is called “Board for adjusting the speed of collector motors without loss of power.”
But we noticed one peculiarity: this board is applicable only for commutator electric motors (with electronic brushes). Naturally, such motors are much less common in everyday life than asynchronous ones. But they have found wide application in automatic washing machines. This is exactly why this scheme was made. Especially for the electric motor from an automatic washing machine. Their power is quite decent, from 200 to 800 watts. This allows them to be used quite widely in everyday life.
This product has already found wide application in people’s households and is widely used by people engaged in various hobbies and professional activities.
READ Drill Attachment for Mixing Concrete
Answering the question - Where can I use the motor from a washing machine? A certain list was formed. Homemade wood lathe; Grinder; Electric drive for concrete mixer; Sharpener; Electric drive for honey extractor; Straw cutter; Homemade pottery wheel; Electronic lawn mower; Wood splitter and much more where mechanical rotation of any devices or objects is needed. And in all these cases, this board “Adjusting the speed of electric motors with maintaining power on the TDA1085” helps us.