Semi-automatic welding (MIG) is a kind of evolution of manual arc welding (MMA). Even despite the availability of MMA inverters, it is better to use MIG welding for home use. But to fully appreciate its advantages, you need to know how to cook with a semi-automatic device. In fact, there is nothing complicated about it.
Semi-automatic welding
For semi-automatic welding of metal, special wire and shielding gas are used. Gas is supplied to the torch through the welding sleeve along with the wire, protecting the weld pool from the external environment.
Electrode wire is produced in reels. Its thickness:
- 0.6 mm;
- 0.8 mm;
- 1 mm;
- 1.2 mm.
For metals thinner than 4 mm, wire 0.6-0.8 mm is used, thicker - 1-1.2 mm.
The shielding gas is carbon dioxide or a mixture of CO2 and argon. Pure carbon dioxide is cheaper - but the weld is worse and welding produces more splashes than when using a mixture with argon.
Features of semi-automatic welding:
- automatic feeding of welding wire – increases the speed and quality of welding;
- welds thin metal - the thickness of the workpiece starts from 0.5 mm;
- versatility - a semi-automatic machine welds steel, stainless steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals;
- there is no slag on the finished welding joint;
- There is virtually no smoke during welding.
On the other hand, the semi-automatic is bulky due to the gas cylinder. In addition, in a strong wind it will not be possible to cook in a gas environment - the wind will blow carbon dioxide out from under the burner.
Semi-automatic welding in a protective environment
If you weld correctly with a semi-automatic machine, you can join galvanized or rusted workpieces. In this case, aluminum or copper filler wire is used to obtain a high-quality, uniform weld.
Before cooking semi-automatic workpieces in a gas environment or using flux, you must:
- clean the joints from dirt, rust, etc., degrease them with a solvent;
- check the operation of gas equipment;
- weld a small section of the joint, if necessary, adjust the equipment settings;
- select the optimal voltage and current.
The easiest way is to cook it correctly with a semi-automatic device in a protective environment of inert gases (argon, helium, nitrogen, carbon dioxide). The gas used does not affect the selected welding technique. Carbon dioxide is most often used because it has good protective properties and a fairly low cost.
Semi-automatic welding of metal workpieces in a shielding gas environment has the following advantages:
- unchanged appearance of the finished structure;
- the ability to process hard-to-reach areas of workpieces;
- thin and durable welded seam;
- minimal amount of waste;
- high speed of work.
The quality of the weld is influenced by the correct distance between the parts being welded, the supply of additive along the joint, and compliance with the work technology.
What you need to know about semi-automatic welding
Before cooking, you need to take into account the intricacies of the welding machine.
How to cook with a semi-automatic machine:
- the positive terminal is connected to the burner, the negative terminal to the workpiece;
- For each type of metal, a special wire is used. For example, for aluminum - aluminum, for stainless steel - stainless steel, etc.;
- Amperage and wire feed speed are mutually related settings. The higher the current, the higher the speed and vice versa;
- The current collecting tip used on the torch must match the diameter of the wire. This part is a consumable item and therefore requires periodic replacement;
- the quality of the seam depends on the settings of the wire feeding mechanism;
- the hose feeding the wire must be rigid - otherwise it may bend and the wire feeding will stop;
- It is better to weld metal thinner than 1 mm in spots if you do not need to get a sealed seam. This way the workpiece will not overheat and burn out;
- if the network voltage is lower than rated, for example 190 rather than 220 volts, it is better to use wire of a smaller diameter. For example, instead of 0.8, take 0.6 - the machine will cope with it much easier, and the seam will turn out to be of high quality.
- For semi-automatic welding without gas, a special wire is used, and the positive terminal is connected to the workpiece.
When welding in the down position, the torch is held at an angle of approximately 60 degrees relative to the workpiece. The distance to the workpiece is 5-15 mm. The burner is driven away from you – “at an angle forward”.
Before starting work, you need to bite off the tip of the wire protruding from the burner. A ball forms on it, which does not conduct electricity well - it will be more difficult to light the burner.
It is necessary to periodically clean the tip and nozzle of the burner from splashes. If this is not done, the wire feed will become intermittent. Therefore, special silicone aerosols are used that protect surfaces from sticking - you need to spray them inside the burner.
Semi-automatic welding and its varieties
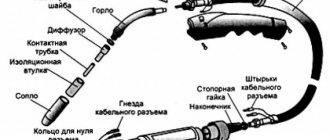
Before cooking with a semi-automatic device, you need to study its design and capabilities in detail. The device itself is made in the form of a mechanical device, where a wire is located, which acts as an electrode, and there is also a mechanism for feeding it automatically.
The speed of wire extension and the current strength can be adjusted on the body of the device, it all depends on the melting temperature of a particular metal, as well as the speed of movement of the torch along the surface to be welded. There are many devices of this type on the market, but the process itself can be divided into two types. Both types have one thing in common - the ability to protect the metal during the welding process:
- Welding under flux layer. Flux is a substance in powder form that is found in the electrode rod. Its chemical properties help protect the process from oxidation.
- A welding process in which welding occurs under the protection of inert gases.
If we distinguish machines by current consumption, then they can be either single- or three-phase. The former are capable of operating from a regular 220 V outlet, but sometimes the device does not have enough power due to frequent power fluctuations, which can lead to an unstable arc and reduce the quality of the seam. The three-phase unit has more stable operation and high quality indicators, but there may be a problem with its connection. Despite the fact that these devices have differences, their equipment is the same:
- Energy source.
- Electrode (wire) feeding mechanism.
- Holder.
- Cable with clip.
- Control block.
- Gas cylinder.
- Gas supply hose.
General rules of welding
As in any business, semi-automatic welding has a base that the welder must know.
- When welding parts with a thickness of more than 3 mm, a gap of 1-2 mm is made between them. This is necessary for complete penetration of the metal. If there is no gap, the seam will be superficial;
- When heated, the metal pulls; to ensure uniformity of the gap, tacks are made on the top and bottom of the workpiece. If the penetration length is large, the number of tacks increases;
- you need to ensure that the seam is evenly deposited on both workpieces.
These are simple rules to remember.
Welding technology
Let us consider in detail the options for welding using a semi-automatic machine. The process of joining metals automatically can be of two types - welding inside a protective gas, and also using wire with powder (flux).
Welding process in the middle of shielding gas
Several types of gas , but carbon dioxide, helium or argon are more often used. Carbon dioxide and helium have low consumption, and are also the most affordable to purchase. The main purpose of the gas is to protect the welded metal from oxidation, which affects the strength properties of the weld. If carbon dioxide is used, the surfaces that will be joined by a seam must be thoroughly cleaned of rust, dust and paint. It is recommended to use a metal brush in combination with sandpaper for this.
Three types of semi-automatic welding:
- Without separation from the metal body . The seam is applied in a continuous layer from the beginning to the intended end.
- Spot welding . The parts are connected by welding points, at specified intervals, along the entire length of the welded surface.
- Short circuit welding . Basically, this type of welding is automatic, and it is applied to thin sheet metal. The process occurs from electrical impulses that the device generates. The short circuit melts the metal and turns it into a drop that connects the parts together.
Semi-automatic welding using carbon dioxide most often takes place in alternating current mode. Before starting work, you need to configure the semi-automatic welding machine. The parameters are adjusted depending on the type of metal. The gas consumption used depends on the current settings of the device. Unlike carbon dioxide, the wire leaves unchanged - the average consumption is 4 cm per second. The exact settings and material consumption can be found in the device’s passport, where, according to GOST, the standards for each type of metal are indicated.
The equipment is configured and ready for work, the parts have been cleaned, and now you can proceed directly to the welding process. The first thing to do is to unscrew the gas supply valve, and only then ignite the arc. Touch the wire to the metal and start the process. The wire is automatically fed each time you press the “Start” button. What determines the quality of the weld? It is important to keep the wire perpendicular to the workpiece, but not to block the view of the seam bath being poured.
It is necessary to maintain the required gap between the parts that are being welded. According to the technology, it looks like this: with a part thickness of up to 10 mm, the gap should not exceed a millimeter, but if the bodies being welded are thicker than one centimeter, then the gap will be 10% of their thickness. It is good to weld parts in a lying position and on an iron gasket, which is placed below close to the base metal.
How to weld aluminum
The semi-automatic machine is also designed for welding aluminum. But there are nuances in this process, due to the fact that such metal has its own characteristics. There is a thin layer of amalgam on the surface of aluminum. Its melting temperature is more than 2 thousand˚C, while the main body melts already at 650˚C. Therefore, argon acts as an inert gas in this case.
When welding aluminum, a special substrate is used for the work - this prevents it from spreading. The welding process is affected by direct current of reverse polarity - a cathode is attached to the part, and the torch plays the role of an anode. This technique improves the quality of melting of the part, and also quickly destroys the amalgam. Although the oxide layer can be removed by simply cleaning the edges of the parts with a fine abrasive.
Welding without the use of inert gas
A distinctive feature of this welding process is that the work can be done both using gas and welding can be done semi-automatically without gas, using ordinary wire. A popular method of welding parts is a seam coated with flux. But more often this method is used in industrial settings, since flux is an expensive material.
Under the influence of a high melting point, the powder creates a cloud of gas, which protects the weld pool from oxidation. And the tap on the inert gas cylinder is closed at this time. The main advantage of flux-cored wire is the ability to carry out the welding process even in strong winds. And in the case of supplying gas from a cylinder, the wind will be a hindrance.
But there are cases where the use of cored wire is not recommended: thin sheet metal and medium carbon steel. There is a danger of defects that may appear in the form of hot cracks. To increase the temperature of the welding arc and high-quality melting of the flux, you need to use the already known technique with reverse polarity - the cathode is placed on the part, the holder with the wire will act as the anode.
Setting up the welding machine
The quality of the weld seam depends on the correct settings of the semi-automatic machine. What needs to be configured:
- Current strength.
- Wire feed speed.
- Gas pressure.
The kit includes instructions that indicate recommended settings for different types of seams and spatial positions. They should be taken as a guide, because... There is no standard that can be applied to all devices. Therefore, the settings are individual. The task is to obtain an even arc, deep penetration and a beautiful welding seam.
Since the wire enters the burner along with carbon dioxide, the gas pressure must be set. It is done within 1-2 atmospheres.
To set up a semi-automatic machine, unnecessary pieces of metal with the same thickness as the main blanks are suitable. A novice master will not be able to immediately set the optimal settings for the device, so experiments need to be carried out on metal that you don’t mind throwing away. A normal seam is smooth and uniform, without interruptions or sharp sagging. The video lessons in the article will help you understand the settings of the semi-automatic machine.
Tabular data values for welding work
There are certain regulations developed empirically, and the table of welding currents for semi-automatic machines will help you make the correct adjustment and setup of the equipment. Below we provide a table that will help you correctly configure the unit based on the specific conditions of working with metal surfaces
| Thickness of welded parts, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Voltmeter readings, V | Ammeter indicators, A | Additive feed rate, m/h |
| 1 -1,5 | 0,8 | 20 | 70-80 | 150 |
| 2 | 1 | 20 | 150-170 | 150 – 180 |
| 3 | 1,2 | 21 | 180-230 | 180 – 240 |
| 4 – 5 | 1,2 | 25 | 200-300 | 350 – 450 |
| 8 | 1,6 | 30 | 300 | 550 – 650 |
This data is quite enough for you to decide how to set up the Resanta semi-automatic welding machine for welding. In any case, these are the recommended settings, and you can adjust more precise settings directly in the workflow.
Gas supply speed
Gas supply setting
Although this parameter is not important and significant, nevertheless, you must control the required gas flow according to the indicators of the reducer, which is installed on the gas-cylinder equipment. It is recommended to set the general gas consumption mode at 6-16 liters. A more precise flow rate will need to be set only if you use a certain thickness of metal in your work.
How many volts do you need to weld?
Now it remains to decide how to configure the Telwin Bimax semi-automatic welding machine using the voltage table data. As you can see, the thicker the metal for welding and cutting, the higher the voltage of the equipment. Using the driven data, the equipment can be configured to efficiently melt and cut metal. Thus, by correctly setting the voltage, we will effectively melt and heat the metal. The only difficulty is if we use non-standard design dimensions in our work, which differ not only in thickness, but also in the main characteristics of the metal connections.
Semi-automatic voltage selection
For highly alloyed materials and non-ferrous metals, you can find data on the Internet. Some users say in bewilderment why a large voltage range from 1 to 10 is indicated for the same material. In this case, it is necessary to be guided by the technical data of the equipment manufacturer, as well as the specifics of welding work.
Wire feed speed mode
The high-speed wire feeding mode is an auxiliary solution to the question of how to set up a semi-automatic welding machine Svarog. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the feed speed together with the strength of the current used. Both slave parameters are interconnected. The higher the current, the faster the wire feeds. At the same time, the quality of the high-speed feeding mode may drop for one reason if you see strong fusion effects or incorrect shear on the seam. In this case, it is necessary to adjust up or down depending on the further effect of the welding equipment.
Wire feed speed adjustment
Today, the industry produces automatic modes for high-speed wire feeding, but such units, as a rule, are designed for professional work by a welder. For household versions of welding equipment, you will have to solve the problem of how to set up a semi-automatic welding machine Lorch yourself, more precisely, by selecting the appropriate mode on the panel part of the semi-automatic welding device.
Additional fine tuning options
In addition, there are options for additional configuration of equipment adjustment, which involve the implementation of the following options:
- Inductance. This parameter allows you to adjust the basic rigidity of the arc and achieve an effective indicator of seam quality. This parameter is suitable for welding with thin steel sheet materials.
- High/Low. Wire feed speed switches are “fast-slow”, in contrast to the standard wire feed speed mode in the drum. Please note that this functionality is provided in many models of welding equipment, so you will have to carefully study the features of using this effect in practice.
Conclusion
The semi-automatic device has become an indispensable assistant, both in everyday life and in industrial production. To accurately set up the equipment, you need to carefully study the instructions and find the optimal solution for setting up the working equipment in accordance with the criteria for welding and cutting metal. Never be afraid to experiment, but at the same time, always remember fire and electrical safety precautions. Based on the results of experiments, it is possible to construct the necessary adjustment mode for a semi-automatic welding machine in operation.
Types of welding seams
Different types of welds have different settings. The type of weld differs according to the type of connection and the spatial position of the workpieces.
By spatial position:
- horizontal;
- vertical;
- ceiling;
- lower.
By connection type:
- into the joint;
- T-bar;
- overlapping;
- corner.
The simplest joints of workpieces are overlap welding and butt welding in the lower position.
Vertical seam
To fully use welding, you need to know how to weld a vertical seam with a semi-automatic machine. The direction of the vertical seam depends on the thickness of the workpieces:
- The thickness of the workpieces is up to 3 mm - direction from top to bottom.
- Thickness more than 3 mm – direction from bottom to top.
The torch is at an angle of 45 degrees to the workpiece. As a rule, it is necessary to reduce the welding current and wire feed speed compared to welding similar workpieces in the lower position.
To obtain a high-quality weld, the welder is required to withstand 3 things:
- Uniform burner speed.
- Distance from the torch to the workpiece.
- Correct angle.
It is important not to overheat the metal being welded so that it does not flow down. The rest will be done by a semi-automatic welding machine.
Welding thin metal
There is nothing difficult about welding parts up to 1 mm thick. On the contrary, welding thin sheet metal with a semi-automatic welding machine is no more difficult than welding thick sheet metal.
Thin sheet metal is welded in two ways:
- normal – any types of connections;
- riveted - the blanks are laid overlapping and welded through pre-made holes in the top sheet.
There are several rules for such welding:
- current strength and wire feed speed decreases;
- you cannot hold the torch in one place - you will either get an influx of welding bead or burn through the workpieces;
- with the rivet method, welding begins from the center of the lower workpiece. If you start welding from the edges of the top, the metal will simply fill the hole, i.e. can't brew well
If you do not need to obtain a hermetically sealed connection, you do not need to weld with a continuous seam. For thin parts, points with an interval of 1-5 cm are sufficient. The welding process can be seen in the video accompanying the article.
Welding thick metals
When welding workpieces thinner than 4 mm, chamfers are removed from the edges. This is done to obtain deep penetration. The burner is not driven in a straight line, but with slight oscillatory movements. For example, zigzag, spiral, back and forth, etc. This will make the seam deeper and wider.
Rules:
- a gap of 1-2 mm is made between the parts;
- the width of the welding seam should be equal to the thickness of the workpiece (approximately), for example, if 2 parts with a thickness of 6 mm are being welded, the seam should extend 3 mm onto each of them;
If the thickness of the workpieces is more than 5 mm, it may be necessary to cook in several passes. The first seam is made in the center, the second and third - above and below the first seam.
In practice, it is not difficult to understand how to operate a semi-automatic machine. You can get acceptable results already on the first day of training. The main thing is not to be afraid to experiment and remember that the semi-automatic settings are individual for each welder.