My own master 2008-12, page 30
It is almost impossible to imagine carpentry or carpentry work without the use of a whole arsenal of special tools like a planer or jointer, or a sherhebel. Each of these instruments, which are similar in principle, has individuality and a unique character. Today, when mass production takes a leading position and all processes are automated, including in the woodworking industry, hand tools are increasingly becoming a thing of history. It's unlikely that anyone is making stools in their garage these days, but it's time to remember those high school craft lessons and pay homage to the archaic traditional planes. The main components of any plane are: a piece of iron (knife), a block, a wedge. Further, planes can be divided into various groups depending on dimensions, intended purpose and additional equipment.
Planer: device, application
As you can already understand, a jointer is a type of planer. Accordingly, this is a device for processing wood surfaces. The mechanical type of jointer is a simple design, represented by 3 elements: a body, a knife and a handle. The body is most often made of wood, less often - of metal.
The electronic version differs from the mechanical one in a more complex design:
Thrust handle – transmits force;
Bell - connects a vacuum cleaner, which allows you to quickly collect wood shavings during the processing of the product;
Manual screw – allows you to change the depth of planing of the product;
Control buttons – used to set the required parameters;
Side stop – makes it more convenient to adjust the width of the surface;
The sole is in contact with the surface of the wood;
Protective cover – prevents the possibility of damage, etc.
The classification of jointers is very diverse, but, in general, two types can be distinguished:
Manual - an easy-to-use device, which is distinguished not only by its operational efficiency, but also by its low price;
Electric - easy to use and more efficient than the manual version. It has a high price.
ON A NOTE. There are mini-jointers on sale that are used exclusively in domestic conditions: they are convenient due to their modest dimensions and good performance. Professional jointers are used in industry. They are high-performance and durable.
When using a jointer, several rules must be followed to ensure the safety of the user. First, you should carefully secure the workpiece. Secondly, you need to use protective clothing and gloves. Thirdly, you should not place your hands near the cutting area.
Types of tools
The classification is very extensive and is associated with various properties. There are two main types:
- A hand jointer can be found in almost any workshop. Its peculiarity lies in the prostate of the device, as well as its low cost.
- Recently, an electric jointer has often been purchased. This is due to ease of operation, as well as fairly high efficiency in use. The only drawback is the fairly high cost.
Don't miss: Thicknesser machine: purpose, device, types, how to choose
The materials used in the manufacture of the main part may differ significantly. Wooden tools are more common, as they are simple and much cheaper. It is suitable for a home workshop. There are also metal structures designed to work in extremely difficult conditions.
The classification is carried out according to what the task is. Examples include the following devices:
- For working with wooden workpieces that have not been processed in any way before. This variety is called Sherhebel. In most cases, a metal is used that can withstand significant impact.
- If finished parts need to be glued together after processing, then tsinubel is used. This design option is characterized by the fact that the knife has serrations. After planing, small grooves appear on the surface. As practice shows, such a surface is best suited for gluing.
If the resulting products do not need to be glued together in the future, you can use a double or single jointer. The main types of carpentry tools include the following:
- The grinder is represented by a type of design, which is characterized by a shortened body and an increased rake angle, as well as a reduced slot for removing chips. The scope of application is to align the ends and remove various burrs.
- In some cases, a semi-joint is used. It is characterized by a reduced length, but the required width remains. Used when working with large parts.
- The folding belt is used for sampling and quartering. It has a design that has a removable sole. The tool differs from others in width and is a specific design option.
- Zenzubel has a double-sided knife made using high-quality steel. The width of this element is 33 mm.
Mini jointers are also available for sale. It is often used in domestic settings, as it is small in size and has sufficient performance. In addition, all devices can be divided into two main groups:
- Household is characterized by low cost, as well as reduced performance characteristics. It is widespread because it costs less.
- A professional jointer is used for work in industry. Its main qualities include increased productivity, as well as the ability to work for a long period.
The production of the instrument in question is carried out by a variety of companies. There is also an industrial jointer that can be used for a long period.
What is the difference between a sherhebel and a planer?
In essence, a sherhebel is the same plane, only intended for rough processing of wood. The sherhebel differs from the plane in the semicircular sharpening of the blade, as well as in its width - the sherhebel has a smaller blade than the plane. At the same time, it protrudes from the block by 2-3mm.
- A jointer is a hand plane with a double cutter. The purpose of the device is the final and precise processing of wood when leveling the plane of a significant volume due to a longer block, as well as for jointing edges. On average, the length of the block can exceed 2-3 times the size of a standard plane. The jointer knife is equipped with a chip breaker and a handle to facilitate operation of the device. The jointer can be produced with either a single or double knife.
Types of tools
The device comes in two types: manual and electric.
Manual jointer
This is a metal or wooden tool, the design of which includes:
- frame;
- handle holder;
- blade (knife).
The length of the block is 90 cm, and the width of the blades is 8 cm. For mini-models, semi-jointers, the length of the sole does not exceed 50 cm. This is convenient for processing large parts.
A type of jointing tool is sherhebel. As standard, it has a 35mm wide blade. The tool is used for primary processing of the workpiece. Scherhebel removes chips 2–3 mm thick.
Another type of jointer is a folding joint. Its narrow, replaceable soleplate is suitable for processing folds, quarters and rebates. Zenzubel is equipped with two knives for cleaner surface grinding of small parts.
Electric
This is not a machine, but a hand-held electrical device.
It takes force to trim the workpiece. Professionals often use an electric jointer. It has:
- Greater mass and clamping force.
- Processes workpieces more precisely.
- The work goes much faster.
- The tool has a set of replaceable attachments.
Don't miss: Principle of choosing an electric planer
A special feature of using an electric jointer is the ability to attach it to a workbench. The result is a machine that replaces special stationary equipment. It is convenient for home or small workshop.
What common
Both tools have a common type of design, and the types of work for which they are used are also similar. In addition, both devices have the same components: a block and a knife, pressed tightly with a wedge. The position of the cutter in both tools can be adjusted, which allows you to vary the thickness of the cut chips.
A jointer can be safely called a type of plane designed for more delicate work. Also, both of these instruments eventually acquired electrical analogues, which can be considered another common feature.
Half jointers, their varieties
It is believed that everything up to 50 cm in length is a semi-jointer. Let's consider the number classification of this interesting instrument.
Semi-jointer No. 5
No. 5 is a very interesting tool. Planers do not differ much from each other, nor do semi-jointers. But the difference between semi-jointers No. 5 and No. 6 is very big. They have a big difference in blade width by a whole centimeter. On the one hand, they can be placed side by side, but they can be classified differently. The logic to classify semi-jointer No. 5 as planes is very simple - the width of the piece of iron is the same. The logic for classifying No. 6 as a jointer is also the same - the width of the blade. But nevertheless, it is a semi-jointer.
A few words about No. 5. The fact is that if in Russia the most common standard size of four is characteristic, then in the Western tradition, for example, multi-purpose planes No. 5 were no less popular among the British. In the English tradition, a jack of all trades who can do anything was called a Jack. This literary name is associated with the name of plane No. 5 - jack. The Five copes excellently with all the most common tasks. Thanks to its length and width of the blade, it planes easier and more evenly than the other number.
Semi-jointer No. 6 is often used by women for carpentry work
#6 from experience can be used in different ways. If we classify it as a jointer, then we can present it as a women's jointer. It is still much shorter than the standard one and therefore lighter. This is his first advantage. Its second advantage is that it is a tool that planes fairly evenly, but due to its small size, relative to jointers, it is convenient to take it with you anywhere on the go. But its most striking manifestation is that it is suitable for planing shields. The boards are planed not only along the grain, but across and at 90 degrees. The six is the first instrument that has a wide blade. The wider the piece of iron, the easier it is to plan the shield.
Shields can also be planed using jointers. But they are heavy. After 10-15 minutes of working with it, fatigue sets in. Therefore, six is irreplaceable. If you plan a smooth surface, it will be smooth and, accordingly, even.
Jointer, molding and other types of planes for repairs
We'll tell you about the main types of planes that will be useful for both a professional carpenter and a home craftsman.
Flat planes
Allows you to obtain a smooth surface without burrs, chips and other defects. These types of planes are suitable for the production of building materials, the manufacture of furniture frames and finishing work. Their main feature is a smooth blade without jagged edges or bends.
Single
For even workpieces after rough planing
A simple model with one blade. Easily cuts a thick layer of wood, but can leave small burrs, chips and other defects. Typically used at an intermediate stage - after removing the outer layer of wood and before finishing polishing.
Double
For a smooth surface of the product
This plane has an additional knife - a chipbreaker. It cuts the raised strip of wood into small pieces, preventing it from breaking. The second blade is installed at a distance of 0.2–2 mm from the main one. The closer they are located, the cleaner the planing results.
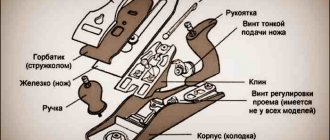
Design
Typically, a plane consists of a sharpened metal blade (“cutter”, “piece of iron”) located at an angle to the surface being processed. The cutter is extended to a certain adjustable length from the tool body (“block”).
- A: Taphole - a slot through which the cutter protrudes and the chips exit;
- B: Cutter (knife, professional - piece of iron) - a sharpened steel plate that cuts material;
- C: Wedge (clamp) - presses the cutter to the plane body;
- D: Cutting depth regulator;
- E: Horn - front handle;
- F: Chipbreaker, wrapping and breaking off chips;
- G: Regulator for cutting uniformity across the width of the plane;
- H: Stop - rear handle;
- I: Index finger rest;
- J: Frog - a plate that allows you to adjust the angle of the cutter. Adjustment is made with a screwdriver with the cutter removed.
Planers have the following design modifications:
- end plane
- has an obliquely set knife for cleaner planing, designed for planing the ends of wood; - rebate
- has a stepped block, designed for processing folds (quarters), that is, rectangular recesses in the edges (for example, recesses for glass in window frames); - zenzubel
- a plane with a narrow block and a special shape of the tap hole (holes for the exit of chips). It has a knife in the shape of a rectangular blade with three cutting edges - the main one and two side ones. Designed for processing grooves and folds; - tongue and groove
- a plane designed for cutting narrow grooves, “tongues” with a width of 2 to 10 mm parallel to the edge of the part. As a rule, it has an adjustable stop on two guides, allowing you to maintain the distance from the edge to the edge of the groove. It has a persistent protrusion under the knife, which allows you to select a thin tongue to a greater depth (the knife does not bend or tremble). Usually the kit includes several knives of different widths; - The additional planer
has three fully working planes (left, bottom, right) and a minimum distance between the front part of the plane and the knife itself.
Design features of planes
You need to start by considering the purpose of the tool. And it is intended for planing wood, that is, to give the wooden surface the desired shape, while eliminating various irregularities, roughness and other defects. The components of the device are:
- Body made of wood or metal - last with sole
- Steel knife, piece of iron or cutter - the main cutting element
- Wedge
- Lever
A more detailed design of a hand plane for wood is shown in the photo below.
The basis of this tool is a cutter, which looks like a rectangular plate with a pointed end. The plate is placed in the block opening at the appropriate angle. A special adjustment mechanism allows you to set the knife to the required distance. This distance is set in order to adjust the cutting depth and chip removal thickness. According to the standard, the blade has a certain sharpening angle, but if the tool is used by a professional, the master sharpens the cutter himself, depending on what type of wood is to be processed.
An equally important element in the design of the tool is the handle. Moreover, a hand plane consists of two handles, one of which is a guide, and the second is a persistent one. The guide handle has a curved design that allows the tool to be grasped by hand. The thrust handle allows you to create the necessary force when performing work.
The body has a smooth surface from which a sharp cutter protrudes. The main condition for the instrument is a perfectly flat and smooth sole. If the sole is not level, then precise processing will simply not be possible. The body of the instrument is made of wood or metal. Home craftsmen give preference to wooden planes, which are cheaper. Woodworkers prefer to work with metal planes, the base of which is made of gray cast iron.
Don't miss: DIY miter saw - making with drawings
Despite the fact that the hand tool in question has a typical design, today more than 10 varieties of these woodworking devices are known. To begin with, it should be noted that all types of planes are divided into two main groups according to the type of drive - manual and electric.
This is interesting! Electric planers are replacing hand tools, but when it comes to planing wood, home craftsmen prefer the second option.
Hand plane knife
A hand plane for wood cannot work without a knife. Such knives operate under conditions of significant loads on the blade. During the reciprocating movement of the tool, the knife cuts into the wood to a specific depth. Since wood is not plastic, chipping of a certain layer occurs and chips are formed. The chips do not have a significant length and quickly split into smaller fractions. This is observed during the “creeping” of wood cut from the workpiece onto the inclined edge of the blade. During the next movement of the plane, a crack appears in the next layer, and so on.
The smaller the span and depth of planing, the smoother and cleaner the workpiece surface is, while at the same time the shear load on the blade is reduced.
Due to the fact that the chips break off when bending upward, the highest stresses are created in the plane block. That is why the block is created from the hardest types of timber.
The knife has a working and a supporting part. The configuration of the working part of the knife includes:
- a chamfer formed on the back of the blade. The chamfer guarantees a reduction in the force of cutting the knife into wood due to the elimination of friction of the rear part against the workpiece material
- front corner. It most often coincides with the accepted tilt of the knife in the plane body
- clearance angle
- working angle of sharpening. It is equal to the difference between the values of the chamfer angle and the angle of inclination of the knife in the plane.
- For the durability of the plane, the most important thing is the rake angle: it is this that ensures the smoothness of the planed surface, the conditions for removing chips from the processing area, as well as the load on the blade itself.
With each passage along the surface, the plane cuts a layer of material to a thickness determined by the amount of extension of the cutter, as well as its angle of inclination.
The plane is a fairly ancient human invention (planes found in Pompeii and dating back to the 1st century are known) [2], although it began to be widely used only in the 15th-16th centuries. The first planes had a wooden block, and the blade was fixed with a wooden wedge. Currently, electric planes are used in industry to perform the same function, since manual planes are not able to provide the necessary performance.
Of course, one of the main parameters is considered to be the sharpening angle of the plane, but it is important to pay attention to other points.
Firstly, the sole of the tool has a serious impact on the final result. If the sole is smooth, then the wood will be planed perfectly.
Secondly, pay attention to the possibility of changing the thickness of the chips removed. Since sharpening hand planes is not always a convenient option, it is better to choose one of the tools, for example, from the MAKITA brand.
What types of planes are there?
Despite the variety of models, woodworking tools are conventionally divided into 3 main categories:
- general purpose;
- for finishing;
- for shape cutting.
Let's look at the representatives of each group in more detail.
General purpose planes
The first tool that a carpenter picks up when starting to process a wooden piece is called a sherhebel.
This is a massive plane in a metal case, designed for rough planing of surfaces that have not previously been treated. The main task of the sherhebel is to give the workpiece the desired shape. A special feature of this plane is deep planing (up to 3 mm), so it will not be possible to achieve a perfectly flat surface.
The blade of this plane has a rounded shape and is usually set at an angle of 45 degrees relative to the sole. The design of the blade allows you to remove chips in a thick layer, working not only along, but also across the wood fibers.
When the workpiece is processed to the required dimensions, the carpenter needs to remove the deep nicks left on the surface by the sherhebel. For these purposes, you can use any of three planes:
- Medvedka is a long tool designed for pair work. It is ideal for leveling massive surfaces or performing large volumes of work;
- jointer is a tool with a double cutter used for finishing leveling wooden surfaces. The length of a manual jointer is approximately 2 times longer than a sherhebel, which allows you to remove chips from a large area in one pass;
- semi-jointer - a shortened analogue of the previous version. A double knife is also used here, and a plane is used to finely level the workpiece.
After processing with these types of planes, the workpiece becomes smooth and even, but far from ideal. Therefore, professionals move on to the next stage of work, picking up another tool.
Finishing planes
Depending on the type of product, 2 planes can be used for finishing planing.
The sander performs final cleaning of the part, eliminating defects remaining from previous planing. The cutting tool is a double knife with a straight blade, sharpened to 60 degrees and equipped with a chipbreaker. Thanks to this structure, it is convenient to plan the surfaces around knots and the end parts of parts with a sander.
Tsinubel is a rather interesting tool that is used to process wooden elements, which are subsequently glued together.
Note! A special feature of the tsinubel is its serrated blade, which leaves neat grooves on the surface.
As a result, a rough surface is formed, providing better adhesion of materials. The zinubel knife is positioned at an angle of 80 degrees, so the surface becomes rough, but burrs and burrs do not appear on it.
In addition, for secondary processing of parts, you can use an end plane, single and double planer. The first is ideal for processing end elements and wood with a complex structure. Single and double hand planes will help remove the nicks left by the sherhebel and level the surface, but after them, in any case, you will have to sand the workpiece.
Shaped cutting
This is a whole series of woodworking tools that make the life of a craftsman who specializes in the manufacture of wooden parts of complex geometric shapes much easier.
For figured cutting, the following hand planes are used:
- zenzubel - designed for planing perpendicular surfaces and quarters, equipped with a double blade made in the form of a spatula;
- federgubel - has a unique blade shape that allows you to create protrusions on the end edges of the product;
- folding belt - used for stripping quarters, has a ribbed sole, and is equipped with straight and oblique knives;
- stabgobel - a plane with a rounded blade for processing concave parts;
- tongue and groove - a structure of two blocks connected by clamping screws, designed to form longitudinal grooves on the edge of the product;
- molding is an indispensable tool for figure cutting, used for making cornices, baguettes, frames for doorways;
- primer – made in the form of a block with a side-mounted cutter, designed to form grooves along wood fibers;
- humpback - has a curved block, which allows you to process the surfaces of the internal and external diameters of products.
Professional carpenters rarely use only one type of plane in their work. To make original products from a piece of wood, you will need to stock up on a full set of tools.
Electric planer
This is a separate type of carpentry tool that combines all the types of hand planes listed above. An electric planer can perform straight and figured planing, ideal for performing large volumes of work.
However, the very use of power tools does not bring inner satisfaction, and their price is sometimes too high. Therefore, if we are talking about building a summer house or putting wood into production, an electric planer is indispensable, but it is unlikely that you will be able to make an original thing for yourself or your loved ones with its help. Only manual processing gives warmth to wood products.