Home / Devices
Back
Reading time: 3 min
1
844
A welding transformer is a classic type of equipment for welding metals. Its history goes back more than 100 years.
The welding transformer has proven to be an unpretentious but reliable technique, capable of welding very thick-walled parts. It has a fairly high level of welding current. In the 21st century, welding transformers have somewhat lost demand.
After all, companies began to produce inverters with suitable functionality and at a relatively low price. However, for the older generation of craftsmen it remains an important tool in their work.
A description of the transformer device for welding metals, its types and application can be found in this article. It will help you understand the basics of welding metals using this machine and select the appropriate model.
As well as mains voltage parameters, functionality, number of work stations and methods for changing current strength.
- general information
- The structure of the transformer apparatus and the principles of its use
- Operating principle of a transformer unit
- Types of transformers for welding metals
- Functionality
- Number of working posts
- Methods for regulating the strength of welding current
- Conclusion
general information
Transformer type welding equipment is a classic among welding equipment.
Its main task is to convert the mains voltage from 220-380V to lower values, or to increase the missing voltage level to operating parameters.
Regardless of the year of manufacture, they are used for manual arc welding using coated electrodes.
The welding transformer is suitable for all types of work, domestic or industrial.
In the twentieth century, this type of welding equipment was used for professional welding, but by the end of the century they began to give way to more compact inverters - equipment of a new generation. But they are still used by many craftsmen.
The advantages of welding transformers include the low cost of the device itself and its parts. Combined with the simplicity of the device, this allows you to carry out repairs yourself in case of malfunctions.
Such devices are quite powerful, capable of welding thick-walled parts. At the same time, they are unpretentious in storage and easy to use.
However, the device also has disadvantages. Large size and weight reduce mobility. Difficulties in ignition and instability of the welded arc affect the speed and quality of the work of an inexperienced craftsman.
There are no switches to adjust the current strength - this occurs by changing the inductive reactance value. Or by adjusting the secondary type of open circuit voltage.
Classification of welding transformers
The division into types of welding transformers is based on the type of welding and phase control. The first feature distinguishes devices for manual arc welding and automatic ones using flux. The second received a more impressive classification, which looks like this:
- Devices with standard magnetic leakage amplitude control (there is an air gap or saturation choke);
- Devices with increased magnetic dissipation (contain movable, spaced apart windings, magnetized capacitors, pulse rectifiers);
- Thyristor (contain pulsed rectifiers or make-up).
We have looked at the general classification of AC welding transformers, which is only superficial. For a more accurate understanding of existing device models, you should understand transformers that differ from each other primarily in phase control.
Devices operating on alternating current with sinusoidal control of the welding process do this by changing the resistance or switching the no-load current. In this case, it is possible to transmit without changes the sinusoidal shape of the input current of transformer welding.
The toroidal transformer is considered one of the most interesting in its design. Its peculiarity is that most of the devices are assembled according to a pattern similar to the letters Ш or П, but this one repeats the shape of a donut. Thanks to this arrangement, it was possible to reduce the size of the device, while obtaining more power from the current volume of the mechanism. Only a three-phase transformer with a step-down system with three single-phase devices can compete with it. This is the most compact and easy to use among the models currently on the market.
All of the above applies to alternating current, but it is also worth mentioning direct current transformers, or rather devices that have an alternating current to direct current rectifier in their design. They are more convenient, produce a stable arc, but working with them requires a certain specialization.
Such mechanisms are rarely used due to the complex operating principle, which not only makes the device heavier, but also makes it prohibitively expensive. Due to the availability of work with non-ferrous metal and stainless steel, DC transformers are most often used in small and large enterprises for processing rare metals. We should not forget that they require special electrodes, so their domestic use is practically excluded. When comparing the two models for AC and DC, the first one should be chosen for personal needs, and the second option is better suited for demanding work in the field of welding services.
The structure of the transformer apparatus and the principles of its use
The transformer consists of 2 units: transformer and regulator. The first is designed to reduce the voltage level that comes from the 220-380V power supply. The second is responsible for setting the required current strength.
There are several types of transformer units. They depend on the voltage level that ensures stable operation of the device. There are three main types of transformers: single-phase, two-phase and three-phase.
The single-phase model is equipped with a core and two windings. A two-phase one consists of two single-phase elements, and a three-phase one contains three single-phase elements.
The control unit consists of a saturation choke. The current is adjusted by changing the gap of the choke magnetic circuit. To do this, you need to remove the case cover, which is not very convenient.
Therefore, craftsmen often modify the transformer on their own, equipping it with an external handle, which is used to regulate the current strength mechanically.
Transformer and control units are the basis of a welding transformer. However, besides them, it includes other devices.
They do not complicate the mechanism too much, so devices of this type rarely suffer from malfunctions. And in the event of a breakdown, you can carry out repairs yourself.
Design features and principle of operation
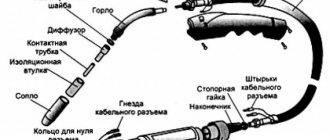
The design of a welding transformer is not particularly complicated. A standard welding apparatus consists of:
- magnetic circuit;
- two windings;
- vertical screw with nut;
- handles;
- clamps for fixing wires;
- metal case.
The principle of operation of a welding transformer is as follows: voltage from the network is supplied to the windings, a magnetic field is formed in them, which, in turn, creates a welding current with the necessary parameters.
Operating principle of a transformer unit
The operating principle of welding devices works on converting current from direct to alternating. This is done in order to ignite the arc.
However, transformer units for welding metals are designed differently. They are devices that perform work using direct welding current. For it, it is enough to adapt the mains voltage to a level suitable for welding.
The transformer unit included in its package copes with this task. With its help, the voltage received from the electrical network is reduced to the operating value.
And the adjustment unit adjusts the strength of the welding current. The principle of operation is simple and clear. An additional element in the work will be grounding.
The principle of working with characteristics
Devices for transformer welding function as follows:
- Current from the electrical network enters the primary winding. Here a magnetic flux appears, directed towards the core.
- The voltage is transmitted to the secondary winding.
- The ferromagnetic core generates a magnetic field. Electromotive forces of a variable nature are generated in 2 windings.
- The difference in the number of turns of the coils helps to change the current parameters to the volt-ampere indicators necessary for welding. Based on these values, the characteristics of the transformer unit are calculated.
The number of turns of the winding is directly related to the output voltage. A secondary coil wound in larger quantities increases the current strength. A transformer welding machine is a step-down device. The number of turns of the primary winding in it is greater than the secondary. You can regulate the output current by changing the gap between the coils.
Idling
The operating principle of the welding transformer includes 2 modes: idle and with load. During welding, the secondary coil creates a short circuit between the workpiece and the electrode. A powerful arc melts the material, forming a seam. After welding is completed, the secondary circuit is broken. The device starts to idle.
Recommended reading: Choosing a chameleon mask
This mode of operation must be safe for the user. The maximum voltage value is 48 V. If the value exceeds the permissible values, the automatic limiter is activated. Grounding the unit body provides additional protection for the welder from electric shock.
Types of transformers for welding metals
The classification of transformer equipment for welding works falls into several categories:
- Mains voltage
- Functional
- Methods for adjusting welding current
- Number of work posts.
- Let's study the classification categories in more detail.
The transformer for arc welding is suitable for power supply from 220-380V mains. Compatibility with different mains voltages depends on the number of phases in the device.
There are 3 types of devices (single-phase, two-phase and three-phase). The first type is compatible with 220V voltage. Three-phase is suitable for working with a 380V outlet. Two-phase models are quite rare.
Combined transformer models work with any mains voltage.
Main technical characteristics of the welding transformer
Before purchasing a welding machine, it is necessary to take into account the following characteristics of the welding transformer:
- Input voltage.
- Power.
- Welding current adjustment range.
- Electrode size.
- Rated value of welding current and voltage.
- Nominal operating mode indicator.
- Type of cooling system.
- Weight and dimensions of the device.
- Open circuit voltage.
You must select the unit in such a way that its parameters correspond to the assigned tasks. Only such equipment will be considered the best.
Functionality
This criterion determines the purpose of the device model. There are 3 types of transformers based on functionality: household, professional and industrial. They have different characteristics and functions.
The residential type has limited 200A capabilities. While the professional one is capable of generating over 300A. This allows them to work with fairly thick metal parts.
For complex tasks, the industrial type of welded transformers is suitable. However, now in industry most of them have been replaced by more technologically advanced models.
Number of working posts
Transformer type welding equipment is used for a different number of work stations. Their number depends on how many welding cables can be connected to the machine.
Conventionally, transformers are divided into two types. Single-post and multi-post. The first type provides one workplace. That is, it is possible to connect only one cable to it for the operation of one master.
The second type is designed to connect 3-6 welding cables, allowing the same number of workers to work simultaneously.
Methods for regulating the strength of welding current
One of the main transformer parts is the adjustment unit, consisting of a saturation choke. It adjusts the strength of the welding current by changing the distance between the coils. But there are other ways to regulate this indicator.
Adjustment of the strength of the welding current is carried out not only using a saturation choke.
You can use a magnetic gap choke, a movable or magnetized shunt, a reactive or dissipative winding, or a movable type of capacitor coil. As well as thyristor regulators or pulse stabilizers.
Varieties of transformer models provide the opportunity to choose the one that suits you. When determining which model to take, it is worth proceeding from the work tasks for which it will be used.
For household work, a single-phase single-station welding unit with a current strength of up to 300A and adjustment by a saturation choke is suitable. These models are easy to use and store.